手写分布式配置中心一步一个脚印正在进行中。
这年头基本上都是使用Spring Boot开发,然后都知道在项目中会有个application.properties配置文件(也有的是application.yaml,反正就是用来保存我们的一些配置信息),通常我们会把一些配置信息写到properties文件中,比如:数据库连接信息、第三方接口信息(密钥、用户名、密码、地址等),连接池、Redis配置信息、各种第三方组件配置信息等。
单体服务,甚至一些小型的分布式架构中,项目的配置都是依赖一个application.properties配置文件来解决(可能有的项目会搞一个环境区分,比如:application-dev.properties、application-pro.properties等)。不过,可能伴随着业务的发展和架构不断升级,服务的数据以及每个服务涉及到配置信息会越来越多,并且对于配置管理的要求也是越来越高,比如配置信息的实时性、独立性等。
同时,我们在微服务架构下,可能还会涉及到不同环境下的配置管理、灰度发布、动态限流、动态降级等需求,包括对于配置内容的安全与权限,所以传统的配置维护方式很难达到需求。
于是,分布式配置中心就在这样的环境下产生了。
本文我们先搞清楚java中读取properties配置文件,到底有哪些方法。
Java读取properties配置文件的6种方式
需求背景
需求是我们项目中有个jdbc.properties 配置文件,内如如下:
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver jdbc.url=mysql://localhost:3306/database?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai jdbc.username=root jdbc.password=123456
现在是想要在java代码中获取上面配置文件内容。
第一种方式
第一种方式我们采用:this.getClass().getResourceAsStream()+Properties
代码实现:
/** * @author tianwc 公众号:java后端技术全栈、面试专栏 * @version 1.0.0 * @date 2023年05月27日 09:13 * 在线刷题1200+,100+篇干货文章:博客地址 */ public void readProperties1() throws IOException { //不加/会从当前包进行寻找,加上/会从src开始找 InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getResourceAsStream("/jdbc.properties"); Properties properties=new Properties(); properties.load(inputStream); System.out.println("jdbc.driver="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.driver")); System.out.println("jdbc.url="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.url")); System.out.println("jdbc.username="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.username")); System.out.println("jdbc.password="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.password")); }
下面来聊聊上面的这段代码:
this.getClass().getResourceAsStream()
具体文件和代码的位置是,代码在
src/main/java目录下,资源文件在src/main/resources/目录下。会从当前类的目录下去找,这个文件如果不和该类在一个目录下,就找不到。
会从编译后的整个classes目录下去找,maven也会把资源文件打包进classes文件夹,所以可以找到。
ClassLoader就是从整个classes文件夹找的,所以前面无需再加/
Properties
Properties:java.util.Properties,该类主要用于读取Java的配置文件,不同的编程语言有自己所支持的配置文件,配置文件中很多变量是经常改变的,为了方便用户的配置,能让用户够脱离程序本身去修改相关的变量设置。就像在Java中,其配置文件常为.properties文件,是以键值对的形式进行参数配置的。
类关系图:
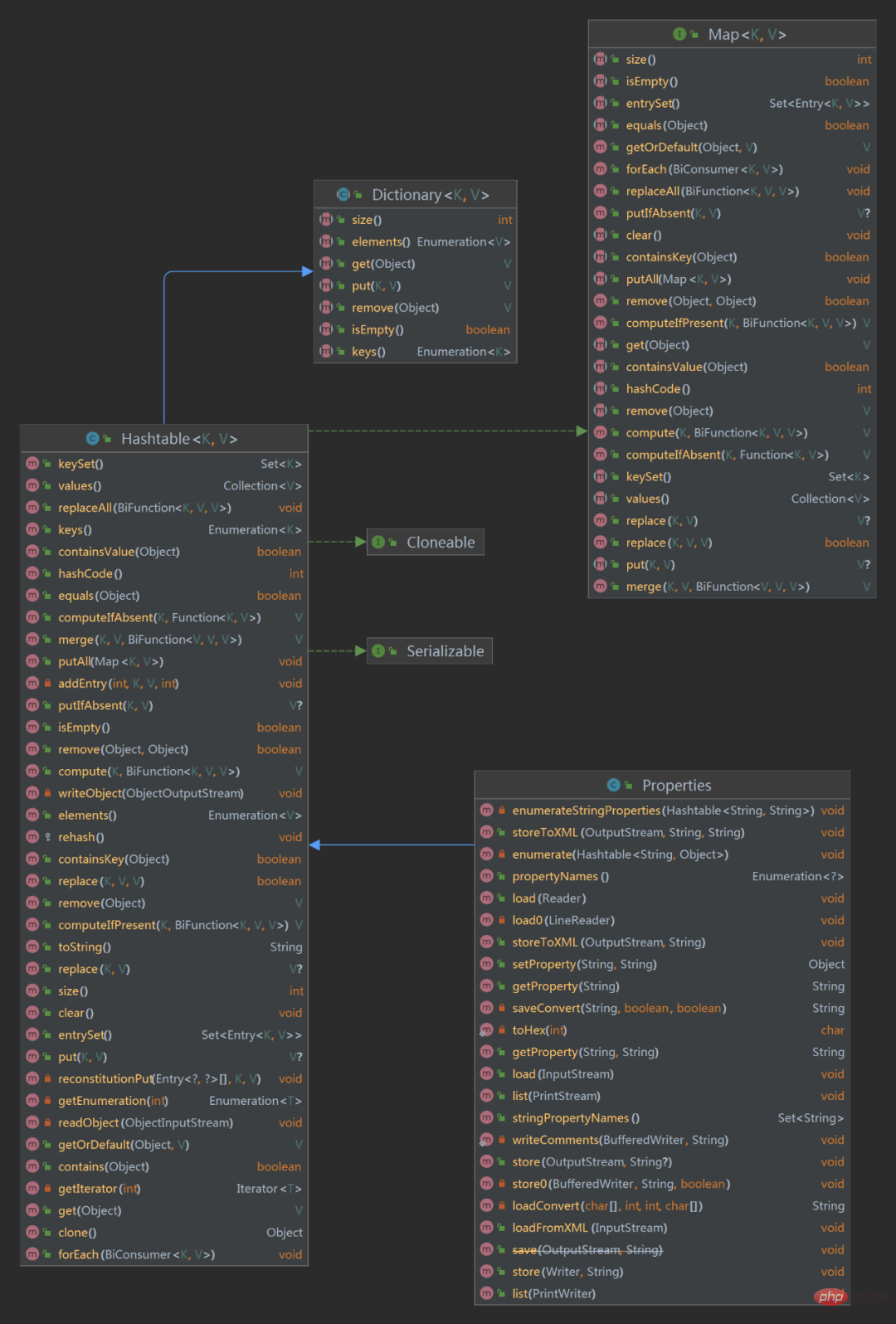
从上面的类图可以看到Properties类继承至Hashtable,相信大家都知道Hashtable是存储key-value数据结构类,也刚好对应我们properties文件内容也是key-value形式。
Properties 常见方法
getProperty(String key) :在此属性列表中搜索具有指定键的属性。如果在此属性列表中找不到该键,则会检查默认属性列表及其默认值(递归)。如果未找到该属性,则该方法返回默认值参数。
list(PrintStream out) 将此属性列表打印到指定的输出流。此方法对于调试很有用。
load(InputStream inStream) :从输入字节流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)。输入流采用加载(Reader)中指定的简单的面向行的格式,并假定使用ISO 8859-1字符编码;即每个字节是一个Latin1字符。不在Latin1中的字符和某些特殊字符在使用Unicode转义符的键和元素中表示。 此方法返回后,指定的流仍保持打开状态。
setProperty(String key, String value) :调用 Hashtable 的方法 put 。他通过调用基类的put方法来设置 键值对。
store(OutputStream out, String comments) :将此Properties表中的此属性列表(键和元素对)以适合使用load(InputStream)方法加载到Properties表的格式写入输出流。 此Properties方法不会写出此Properties表的defaults表中的属性(如果有)。
storeToXML(OutputStream os, String comment, String encoding) :使用指定的编码发出表示此表中包含的所有属性的XML文档。
clear() :清除此哈希表,使其不包含任何键。
stringPropertyNames() :返回此属性列表中的一组键,其中键及其对应的值是字符串,如果尚未从主属性列表中找到相同名称的键,则包括默认属性列表中的不同键。键或键不是String类型的属性将被省略。
properties.load(inputStream)
public synchronized void load(InputStream inStream) throws IOException {
load0(new LineReader(inStream));
}
private void load0 (LineReader lr) throws IOException {
char[] convtBuf = new char[1024];
int limit;
int keyLen;
int valueStart;
char c;
boolean hasSep;
boolean precedingBackslash;
//逐行读取
while ((limit = lr.readLine()) >= 0) {
c = 0;
keyLen = 0;
valueStart = limit;
hasSep = false;
//System.out.println("line=<" + new String(lineBuf, 0, limit) + ">");
precedingBackslash = false;
while (keyLen < limit) {
c = lr.lineBuf[keyLen];
//need check if escaped.
if ((c == '=' || c == ':') && !precedingBackslash) {
valueStart = keyLen + 1;
hasSep = true;
break;
} else if ((c == ' ' || c == '\t' || c == '\f') && !precedingBackslash) {
valueStart = keyLen + 1;
break;
}
if (c == '\\') {
precedingBackslash = !precedingBackslash;
} else {
precedingBackslash = false;
}
keyLen++;
}
while (valueStart < limit) {
c = lr.lineBuf[valueStart];
if (c != ' ' && c != '\t' && c != '\f') {
if (!hasSep && (c == '=' || c == ':')) {
hasSep = true;
} else {
break;
}
}
valueStart++;
}
//前面一堆代码就是做校验和解析
//下面两个是做转换
String key = loadConvert(lr.lineBuf, 0, keyLen, convtBuf);
String value = loadConvert(lr.lineBuf, valueStart, limit - valueStart, convtBuf);
put(key, value);
}
}最后调用put(key, value);这个put方法就是Hashtable中的put方法。这里可以这么理解:将我们的配置项保存到Hashtable中。
getProperty(String key)
public String getProperty(String key) {
Object oval = super.get(key);
String sval = (oval instanceof String) ? (String)oval : null;
return ((sval == null) && (defaults != null)) ? defaults.getProperty(key) : sval;
}super.get(key);就是调用Hashtable中的get()方法,也就是此时返回value,同时这就对应返回了properties文件中key对应的value。
第二种方式
第二种方式,我们通过当前类的加载器进行读取this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream()获取InputStream。
代码实现:
/** * @author tianwc 公众号:java后端技术全栈、面试专栏 * @version 1.0.0 * @date 2023年05月27日 09:13 * 博客地址:在线刷题1200+,100+篇干货文章 */ public void readProperties2() throws IOException { //不加/,若加了会为null InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); //如果放在config目录下 //InputStream inputStream = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("config/jdbc.properties"); Properties properties=new Properties(); properties.load(inputStream); System.out.println("jdbc.driver="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.driver")); System.out.println("jdbc.url="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.url")); System.out.println("jdbc.username="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.username")); System.out.println("jdbc.password="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.password")); }
第一看怎么觉得和第一种方式很像,下面来说说两个的区别。
this.getClass.getResourceAsStream()从当前类所在的位置开始查找配置文件位置。要找到jdbc.properties必须加/从classpath下开始查找this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream()默认就从classpath路径下开始查找,加上/会报空指针异常。
剩下的部分代码和第一种方式一样,这里就不在赘述了。
第三种方式
接下来我们采用ClassLoader类的static方法 getSystemResourceAsStream()。
/** * @author tianwc 公众号:java后端技术全栈、面试专栏 * @version 1.0.0 * @date 2023年05月27日 09:13 * 博客地址:在线刷题1200+,100+篇干货文章 */ public void readProperties3() throws IOException { //如果存放到config目录下 //InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("config/jdbc.properties"); InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties"); Properties properties=new Properties(); properties.load(inputStream); System.out.println("jdbc.driver="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.driver")); System.out.println("jdbc.url="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.url")); System.out.println("jdbc.username="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.username")); System.out.println("jdbc.password="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.password")); }
ClassLoader中的
getSystemResourceAsStream()方法,它用于获取资源作为参数并将资源转换为InputStream。例如,我们可以使用该方法获取网站的静态资源并将其转换为InputStream。
说白了就是获取InputStream的方式不同罢了,最终还是交给Properties去解析jdbc.properties文件内容。
第四种方式
我们在实际开发中,基本上都是离不开Spring了,所以,接下来我们使用Spring中的 ClassPathResource读取配置文件。
代码实现:
/** * @author tianwc 公众号:java后端技术全栈、面试专栏 * @version 1.0.0 * @date 2023年05月27日 09:13 * 博客地址:博客地址 */ public void readProperties4() throws IOException { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("jdbc.properties"); //ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("config/jdbc.properties"); Properties properties= PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); System.out.println("jdbc.driver="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.driver")); System.out.println("jdbc.url="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.url")); System.out.println("jdbc.username="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.username")); System.out.println("jdbc.password="+properties.getProperty("jdbc.password")); }
这里PropertiesLoaderUtils是spring-core.jar下面的,全路径名称:
org.springframework.core.io.support.PropertiesLoaderUtils。
PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource)源码部分:
public static Properties loadProperties(EncodedResource resource) throws IOException {
//创建一个Properties对象
Properties props = new Properties();
//处理文件内容并赋值给props
fillProperties(props, resource);
return props;
}fillProperties(props, resource);方法:
public static void fillProperties(Properties props, EncodedResource resource) throws IOException {
fillProperties(props, resource, ResourcePropertiesPersister.INSTANCE);
}
static void fillProperties(Properties props, EncodedResource resource, PropertiesPersister persister) throws IOException {
InputStream stream = null;
Reader reader = null;
try {
//省略不相关代码
stream = resource.getInputStream();
//获取InputStream
persister.load(props, stream);
} finally {
//关闭
}
}最后到PropertiesPersister的persister.load(props, stream);
public void load(Properties props, InputStream is) throws IOException {
props.load(is);
}这里又回到Properties类中的load()方法里了。
绕了半天也只是获取
InputStream的方式不同而已
第五种方式
接下来我们来使用PropertyResourceBundle读取InputStream流,实现配置文件读取。
代码实现:
public void readProperties5() throws IOException {
InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
//InputStream inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("config/jdbc.properties");
PropertyResourceBundle bundle = new PropertyResourceBundle(inputStream);
System.out.println(bundle.getString("jdbc.driver"));
System.out.println(bundle.getString("jdbc.url"));
System.out.println(bundle.getString("jdbc.username"));
System.out.println(bundle.getString("jdbc.password"));
}好像也没什么,
PropertyResourceBundle源码
我们来看看 new PropertyResourceBundle(inputStream);源码部分:
public PropertyResourceBundle (InputStream stream) throws IOException {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(stream);
lookup = new HashMap(properties);
}这个构造方法里直接new了一个Properties对象。然后调用load方法解析。
所以,这种方式无非就是在Properties基础之上再封装了,也就是让我们使用起来更加方便。
PropertyResourceBundle类关系图
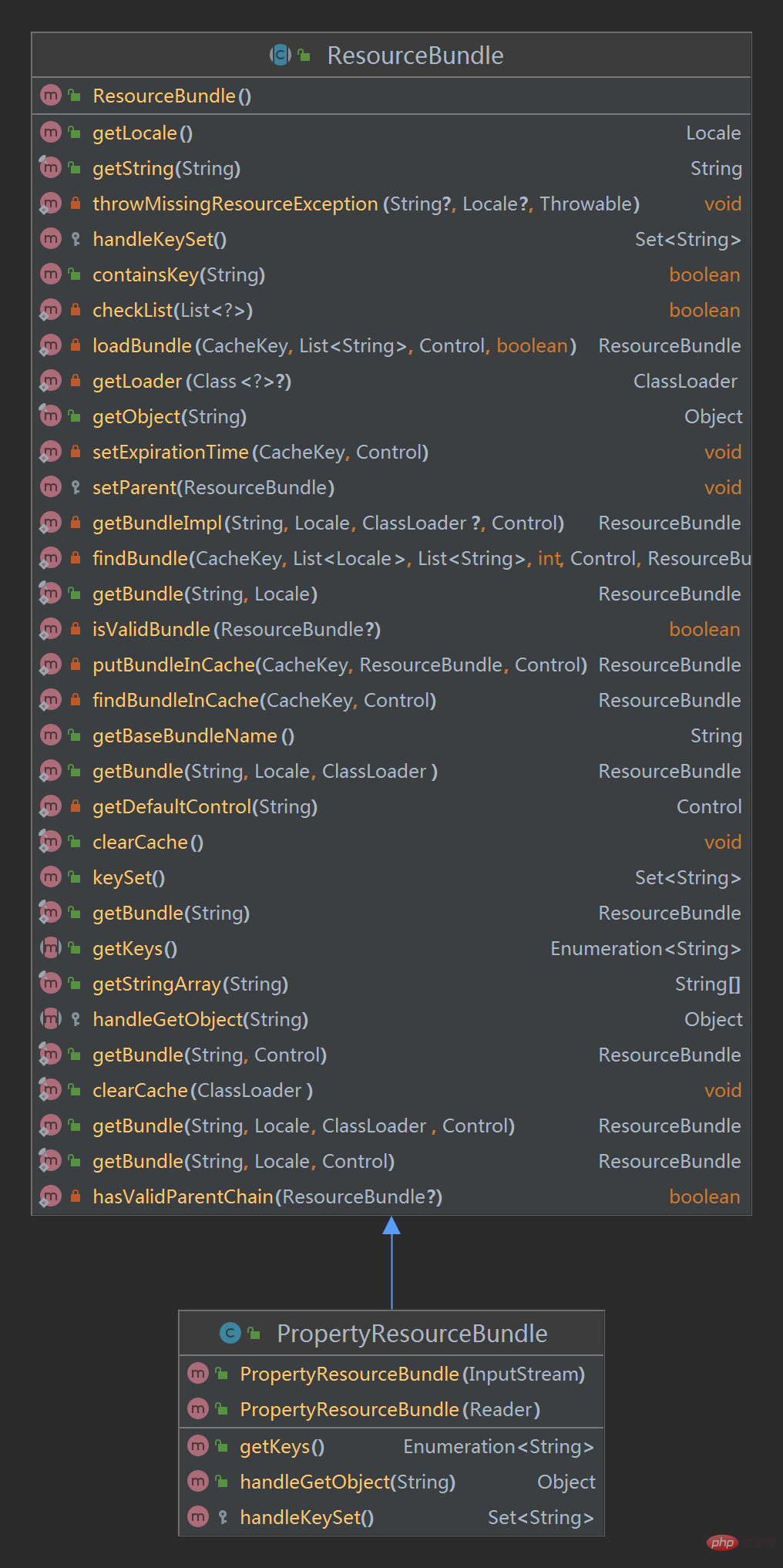
所以,上面代码中的bundle.getString("jdbc.url")其实调用的是父类中方法;
public final String getString(String key) {
return (String) getObject(key);
}最终调用到PropertyResourceBundle的handleGetObject()方法:
public Object handleGetObject(String key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
return lookup.get(key);
}lookup就是一个HashMap:lookup = new HashMap(properties);
第六种方式
第五种方式中我们看到了ResourceBundle,接下来我们就是用ResourceBundle.getBundle()实现。
//不用输入后缀
public void readProperties6() {
ResourceBundle bundle=ResourceBundle.getBundle("jdbc");
System.out.println(bundle.getString("jdbc.driver"));
System.out.println(bundle.getString("jdbc.url"));
System.out.println(bundle.getString("jdbc.username"));
System.out.println(bundle.getString("jdbc.password"));
}直接使用文件名称就可以了,不需要写文件后缀名。
java.util.ResourceBundle.getBundle(String baseName)方法获取使用指定的基本名称,不需要文件后缀名,默认的语言环境和调用者的类加载器获取资源包。
如果 baseName为 null ,则报异常NullPointerException如果可以找到指定的基没有相应的资源包 ,则报异常 MissingResourceException
总结
以上就是我们通常在java中读取properties文件的6中方式。


























