本篇文章主要介绍了.properties文件读取及占位符${...}替换源码解析的相关知识,具有很好的参考价值。下面跟着小编一起来看下吧
前言
我们在开发中常遇到一种场景,Bean里面有一些参数是比较固定的,这种时候通常会采用配置的方式,将这些参数配置在.properties文件中,然后在Bean实例化的时候通过Spring将这些.properties文件中配置的参数使用占位符"${}"替换的方式读入并设置到Bean的相应参数中。
这种做法最典型的就是JDBC的配置,本文就来研究一下.properties文件读取及占位符"${}"替换的源码,首先从代码入手,定义一个DataSource,模拟一下JDBC四个参数:
public class DataSource {
/**
* 驱动类
*/
private String driveClass;
/**
* jdbc地址
*/
private String url;
/**
* 用户名
*/
private String userName;
/**
* 密码
*/
private String password;
public String getDriveClass() {
return driveClass;
}
public void setDriveClass(String driveClass) {
this.driveClass = driveClass;
}
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getUserName() {
return userName;
}
public void setUserName(String userName) {
this.userName = userName;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "DataSource [driveClass=" + driveClass + ", url=" + url + ", userName=" + userName + ", password=" + password + "]";
}
}定义一个db.properties文件:
driveClass=0 url=1 userName=2 password=3
定义一个properties.xml文件:
写一段测试代码:
public class TestProperties {
@Test
public void testProperties() {
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring/properties.xml");
DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)ac.getBean("dataSource");
System.out.println(dataSource);
}
}运行结果就不贴了,很明显,下面就来分析一下Spring是如何将properties文件中的属性读入并替换"${}"占位符的。
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer类解析
在properties.xml文件中我们看到了一个类PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,顾名思义它就是一个属性占位符配置器,看一下这个类的继承关系图:
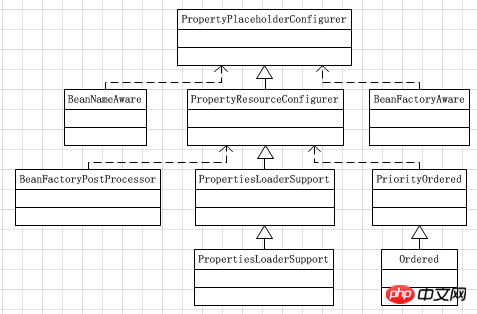
看到从这张图上,我们能分析出来的最重要的一点就是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer是BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类,想见Spring上下文必然是在Bean定义全部加载完毕后且Bean实例化之前通过postProcessBeanFactory方法一次性地替换了占位符"${}"。
.properties文件读取源码解析
下面来看一下postProcessBeanFactory方法实现:
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
Properties mergedProps = mergeProperties();
// Convert the merged properties, if necessary.
convertProperties(mergedProps);
// Let the subclass process the properties.
processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}跟一下第3行的mergeProperties方法:
protected Properties mergeProperties() throws IOException {
Properties result = new Properties();
if (this.localOverride) {
// Load properties from file upfront, to let local properties override.
loadProperties(result);
}
if (this.localProperties != null) {
for (Properties localProp : this.localProperties) {
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(localProp, result);
}
}
if (!this.localOverride) {
// Load properties from file afterwards, to let those properties override.
loadProperties(result);
}
return result;
}第2行的方法new出一个Properties,名为result,这个result会随着之后的代码传入,.properties文件中的数据会写入result中。
OK,接着看,代码进入第17行的方法,通过文件加载.properties文件:
protected void loadProperties(Properties props) throws IOException {
if (this.locations != null) {
for (Resource location : this.locations) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Loading properties file from " + location);
}
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = location.getInputStream();
String filename = null;
try {
filename = location.getFilename();
} catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// resource is not file-based. See SPR-7552.
}
if (filename != null && filename.endsWith(XML_FILE_EXTENSION)) {
this.propertiesPersister.loadFromXml(props, is);
}
else {
if (this.fileEncoding != null) {
this.propertiesPersister.load(props, new InputStreamReader(is, this.fileEncoding));
}
else {
this.propertiesPersister.load(props, is);
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
if (this.ignoreResourceNotFound) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Could not load properties from " + location + ": " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
else {
throw ex;
}
}
finally {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
}
}
}
}第9行,PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer的配置可以传入路径列表(当然这里只传了一个db.properties),第3行遍历列表,第9行通过一个输入字节流InputStream获取.properties对应的二进制数据,然后第23行的代码将InputStream中的二进制解析,写入第一个参数Properties中,Properties是JDK原生的读取.properties文件的工具。
就这样一个简单的流程,将.properties中的数据进行了解析,并写入result中(result是mergeProperties方法中new出的一个Properties)。
占位符"${...}"替换源码解析
上面看了.properties文件读取流程,接着就应当替换"${}"占位符了,还是回到postProcessBeanFactory方法:
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
Properties mergedProps = mergeProperties();
// Convert the merged properties, if necessary.
convertProperties(mergedProps);
// Let the subclass process the properties.
processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}第3行合并了.properties文件(之所以叫做合并是因为多个.properties文件中可能有相同的Key)。
第6行在必要的情况下对合并的Properties进行转换,没看出有什么用。
第9行就开始替换占位符"${...}"了,要事先声明一点:BeanFactoryPostProcessor类的postProcessBeanFactory方法调用是在Bean定义解析之后,因此当前的beanFactory参数中已经有了所有的Bean定义,如果熟悉Bean解析流程的朋友对这一点应该很清楚。跟一下第9行的processProperties方法:
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, Properties props)
throws BeansException {
StringValueResolver valueResolver = new PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver(props);
BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor(valueResolver);
String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String curName : beanNames) {
// Check that we're not parsing our own bean definition,
// to avoid failing on unresolvable placeholders in properties file locations.
if (!(curName.equals(this.beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this.beanFactory))) {
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName);
try {
visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
// New in Spring 2.5: resolve placeholders in alias target names and aliases as well.
beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver);
// New in Spring 3.0: resolve placeholders in embedded values such as annotation attributes.
beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);
}第4行new出一个PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver,传入Properties,顾名思义这是一个持有.properties文件配置的字符串值解析器。
第5行BeanDefinitionVistor,传入上面的StringValueResolver,顾名思义这是一个Bean定义访问工具,持有字符串值解析器,想见可以通过BeanDefinitionVistor访问Bean定义,在遇到需要解析的字符串的时候使用构造函数传入的StringValueResolver解析字符串。
第7行通过BeanFactory获取所有Bean定义的名称。
第8行开始遍历所有Bean定义的名称,注意第11行的第一个判断"!(curName.equals(this.beanName)" ,this.beanName指的是PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,意为PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer本身不会去解析占位符"${...}"。
着重跟14行的代码,BeanDefinitionVistor的visitBeanDefinition方法,传入BeanDefinition:
public void visitBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
visitParentName(beanDefinition);
visitBeanClassName(beanDefinition);
visitFactoryBeanName(beanDefinition);
visitFactoryMethodName(beanDefinition);
visitScope(beanDefinition);
visitPropertyValues(beanDefinition.getPropertyValues());
ConstructorArgumentValues cas = beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
visitIndexedArgumentValues(cas.getIndexedArgumentValues());
visitGenericArgumentValues(cas.getGenericArgumentValues());
}看到这个方法轮番访问
protected void visitPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
PropertyValue[] pvArray = pvs.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue pv : pvArray) {
Object newVal = resolveValue(pv.getValue());
if (!ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(newVal, pv.getValue())) {
pvs.add(pv.getName(), newVal);
}
}
}获取属性数组进行遍历,第4行的代码对属性值进行解析获取新属性值,第5行判断新属性值与原属性值不等,第6行的代码用新属性值替换原属性值。因此跟一下第4行的resolveValue方法:
protected Object resolveValue(Object value) {
if (value instanceof BeanDefinition) {
visitBeanDefinition((BeanDefinition) value);
}
else if (value instanceof BeanDefinitionHolder) {
visitBeanDefinition(((BeanDefinitionHolder) value).getBeanDefinition());
}
else if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanReference) {
RuntimeBeanReference ref = (RuntimeBeanReference) value;
String newBeanName = resolveStringValue(ref.getBeanName());
if (!newBeanName.equals(ref.getBeanName())) {
return new RuntimeBeanReference(newBeanName);
}
}
else if (value instanceof RuntimeBeanNameReference) {
RuntimeBeanNameReference ref = (RuntimeBeanNameReference) value;
String newBeanName = resolveStringValue(ref.getBeanName());
if (!newBeanName.equals(ref.getBeanName())) {
return new RuntimeBeanNameReference(newBeanName);
}
}
else if (value instanceof Object[]) {
visitArray((Object[]) value);
}
else if (value instanceof List) {
visitList((List) value);
}
else if (value instanceof Set) {
visitSet((Set) value);
}
else if (value instanceof Map) {
visitMap((Map) value);
}
else if (value instanceof TypedStringValue) {
TypedStringValue typedStringValue = (TypedStringValue) value;
String stringValue = typedStringValue.getValue();
if (stringValue != null) {
String visitedString = resolveStringValue(stringValue);
typedStringValue.setValue(visitedString);
}
}
else if (value instanceof String) {
return resolveStringValue((String) value);
}
return value;
}这里主要对value类型做一个判断,我们配置文件里面配置的是字符串,因此就看字符串相关代码,即34行的判断进去,其余的差不多,可以自己看一下源码是怎么做的。第35~第36行的代码就是获取属性值,第38行的代码resolveStringValue方法解析字符串:
protected String resolveStringValue(String strVal) {
if (this.valueResolver == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No StringValueResolver specified - pass a resolver " +
"object into the constructor or override the 'resolveStringValue' method");
}
String resolvedValue = this.valueResolver.resolveStringValue(strVal);
// Return original String if not modified.
return (strVal.equals(resolvedValue) ? strVal : resolvedValue);
}继续跟第6行的方法,valueResolver前面说过了,是传入的一个PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver,看一下resolveStringValue方法实现:
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) throws BeansException {
String value = this.helper.replacePlaceholders(strVal, this.resolver);
return (value.equals(nullValue) ? null : value);
}第2行的replacePlaceholders方法顾名思义,替换占位符,它位于PropertyPlaceholderHelper类中,跟一下这个方法:
public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) {
Assert.notNull(value, "Argument 'value' must not be null.");
return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet());
} 继续跟第3行的parseStringValue方法,即追踪到了替换占位符的核心代码中:
protected String parseStringValue(
String strVal, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set visitedPlaceholders) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(strVal);
int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
while (startIndex != -1) {
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(buf, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
String placeholder = buf.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(placeholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + placeholder + "' in property definitions");
}
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key.
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key...
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the
// previously resolved placeholder value.
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
buf.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
startIndex = buf.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
startIndex = buf.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(placeholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
}
return buf.toString();
} 过一下此流程:
获取占位符前缀"${"的位置索引startIndex
占位符前缀"${"存在,从"${"后面开始获取占位符后缀"}"的位置索引endIndex
如果占位符前缀位置索引startIndex与占位符后缀的位置索引endIndex都存在,截取中间的部分placeHolder
从Properties中获取placeHolder对应的值propVal
如果propVal不存在,尝试对placeHolder使用":"进行一次分割,如果分割出来有结果,那么前面一部分命名为actualPlaceholder,后面一部分命名为defaultValue,尝试从Properties中获取actualPlaceholder对应的value,如果存在则取此value,如果不存在则取defaultValue,最终赋值给propVal
返回propVal,就是替换之后的值
流程很长,通过这样一整个的流程,将占位符"${...}"中的内容替换为了我们需要的值。
【相关推荐】
1. Java免费视频教程
2. 继承0
3. 继承1






























