本文提出基于FFT的动态滤波器令牌混合器DFFormer及混合模型CDFFormer,改进GFNet的自适应能力。动态滤波器结合CondConv思想生成,通过非线性函数预测权重并加权求和。实验显示,CDFFormer在图像识别达85.0%Top-1准确率,高分辨率处理时吞吐量和存储效率优于部分先进架构。
☞☞☞AI 智能聊天, 问答助手, AI 智能搜索, 免费无限量使用 DeepSeek R1 模型☜☜☜

DFFormer:基于快速傅里叶变换的视觉动态令牌混合器
摘要
在计算机视觉领域,具有多头自注意力(MHSA)的模型取得了显著的性能。 它们的计算复杂度与输入特征图中像素的二次方成正比,导致处理速度慢,尤其是在处理高分辨率图像时。 提出了一种新的令牌混合器来代替MHSA来解决这个问题:一种基于FFT的令牌混合器,它在全局操作上与MHSA相似,但计算复杂度较低。 然而,尽管基于FFT的令牌混合器具有诱人的特性,但它与快速发展的MetaFormer体系结构的兼容性还没有得到仔细的研究。 在此,我们提出了一种新的令牌混合器,称为动态滤波器和DFformer和CDFformer,利用动态滤波器的图像识别模型来弥补上述差距。 CDFformer获得了85.0%的Top-1准确率,接近卷积和MHSA的混合架构。 其他广泛的实验和分析,包括对象检测和语义分割,证明它们与最先进的体系结构是有竞争力的; 在处理高分辨率图像识别时,它们的吞吐量和存储效率是卷积和MHSA,与ConvFormer相差不大,远优于CAFormer。 我们的结果表明,动态滤波器是值得认真考虑的令牌混合器选项之一。
1. DFFormer
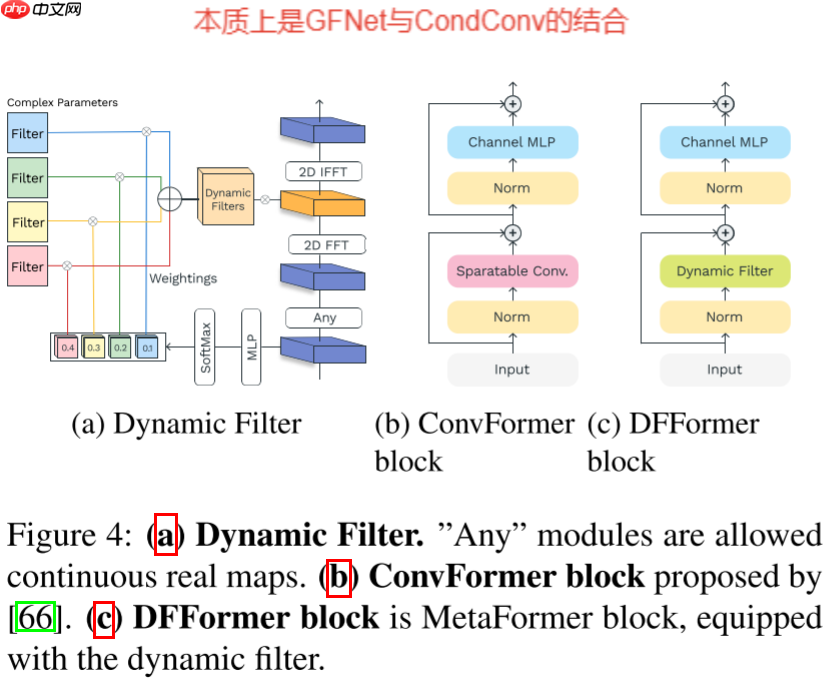
本文针对之前的GFNet无法自适应输入进行改进,结合CondConv提出了一种新的动态滤波器,动态滤波器的总体操作为:
D(X)=F−1(KM(X)⊙F∘A(X))
动态滤波器生成,主要思路与CondConv差不多,即使用一个非线性函数对滤波器权重进行预测,然后将多个滤波器进行加权求和,公式如下所示:
KM(X)c,:,::=∑i=1N(∑n=1Nes(c−1)N+nes(c−1)N+i)Ki, where (s1,…,sNC′)⊤=M(HW∑h,wX:,h,w).
滤波器权重生成公式如下所示:
M(X)=W2StarReLU(W1LN(X))
进而本文基于提出的DFFormer和ConvFormer提出了一种新的混合模型——CDFFormer。
2. 代码复现
2.1 下载并导入所需的库
%matplotlib inlineimport paddleimport numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom paddle.vision.datasets import Cifar10from paddle.vision.transforms import Transposefrom paddle.io import Dataset, DataLoaderfrom paddle import nnimport paddle.nn.functional as Fimport paddle.vision.transforms as transformsimport osimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom matplotlib.pyplot import figurefrom functools import partial
2.2 创建数据集
train_tfm = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224, scale=(0.6, 1.0)),
transforms.ColorJitter(brightness=0.2,contrast=0.2, saturation=0.2),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(0.5),
transforms.RandomRotation(20),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
])
test_tfm = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.485, 0.456, 0.406), std=(0.229, 0.224, 0.225)),
])
paddle.vision.set_image_backend('cv2')# 使用Cifar10数据集train_dataset = Cifar10(data_file='data/data152754/cifar-10-python.tar.gz', mode='train', transform = train_tfm, )
val_dataset = Cifar10(data_file='data/data152754/cifar-10-python.tar.gz', mode='test',transform = test_tfm)print("train_dataset: %d" % len(train_dataset))print("val_dataset: %d" % len(val_dataset))
train_dataset: 50000 val_dataset: 10000
batch_size=128
train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, drop_last=True, num_workers=4) val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, drop_last=False, num_workers=4)
2.3 模型的创建
2.3.1 标签平滑
class LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, smoothing=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.smoothing = smoothing def forward(self, pred, target):
confidence = 1. - self.smoothing
log_probs = F.log_softmax(pred, axis=-1)
idx = paddle.stack([paddle.arange(log_probs.shape[0]), target], axis=1)
nll_loss = paddle.gather_nd(-log_probs, index=idx)
smooth_loss = paddle.mean(-log_probs, axis=-1)
loss = confidence * nll_loss + self.smoothing * smooth_loss return loss.mean()
2.3.2 DropPath
def drop_path(x, drop_prob=0.0, training=False):
"""
Drop paths (Stochastic Depth) per sample (when applied in main path of residual blocks).
the original name is misleading as 'Drop Connect' is a different form of dropout in a separate paper...
See discussion: https://github.com/tensorflow/tpu/issues/494#issuecomment-532968956 ...
"""
if drop_prob == 0.0 or not training: return x
keep_prob = paddle.to_tensor(1 - drop_prob)
shape = (paddle.shape(x)[0],) + (1,) * (x.ndim - 1)
random_tensor = keep_prob + paddle.rand(shape, dtype=x.dtype)
random_tensor = paddle.floor(random_tensor) # binarize
output = x.divide(keep_prob) * random_tensor return outputclass DropPath(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, drop_prob=None):
super(DropPath, self).__init__()
self.drop_prob = drop_prob def forward(self, x):
return drop_path(x, self.drop_prob, self.training)
2.3.3 DFFormer模型的创建
class Downsampling(nn.Layer):
"""
Downsampling implemented by a layer of convolution.
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels,
kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0,
pre_norm=None, post_norm=None, pre_permute=False):
super().__init__()
self.pre_norm = pre_norm(in_channels) if pre_norm else nn.Identity()
self.pre_permute = pre_permute
self.conv = nn.Conv2D(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding)
self.post_norm = post_norm(out_channels) if post_norm else nn.Identity() def forward(self, x):
x = self.pre_norm(x) if self.pre_permute: # if take [B, H, W, C] as input, permute it to [B, C, H, W]
x = x.transpose([0, 3, 1, 2])
x = self.conv(x)
x = x.transpose([0, 2, 3, 1]) # [B, C, H, W] -> [B, H, W, C]
x = self.post_norm(x) return x
class Scale(nn.Layer):
"""
Scale vector by element multiplications.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, init_value=1.0):
super().__init__()
self.scale = self.create_parameter(shape=[dim], default_initializer=nn.initializer.Constant(init_value)) def forward(self, x):
return x * self.scale
class SquaredReLU(nn.Layer):
"""
Squared ReLU: https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.08668
"""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU() def forward(self, x):
return paddle.square(self.relu(x))
class StarReLU(nn.Layer):
"""
StarReLU: s * relu(x) ** 2 + b
"""
def __init__(self, scale_value=1.0, bias_value=0.0):
super().__init__()
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.scale = self.create_parameter(shape=[1], default_initializer=nn.initializer.Constant(scale_value))
self.bias = self.create_parameter(shape=[1], default_initializer=nn.initializer.Constant(bias_value)) def forward(self, x):
return self.scale * self.relu(x) ** 2 + self.bias
def to_2tuple(x):
if isinstance(x, (int, float)):
x = [x, x] return xclass Mlp(nn.Layer):
""" MLP as used in MetaFormer models, eg Transformer, MLP-Mixer, PoolFormer, MetaFormer baslines and related networks.
Mostly copied from timm.
"""
def __init__(self, dim, mlp_ratio=4, out_features=None, act_layer=StarReLU, drop=0.,
bias=False, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
in_features = dim
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = int(mlp_ratio * in_features)
drop_probs = to_2tuple(drop)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features, bias_attr=bias)
self.act = act_layer()
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(drop_probs[0])
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features, bias_attr=bias)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(drop_probs[1]) def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop2(x) return x
class LayerNormGeneral(nn.Layer):
r""" General LayerNorm for different situations.
Args:
affine_shape (int, list or tuple): The shape of affine weight and bias.
Usually the affine_shape=C, but in some implementation, like torch.nn.LayerNorm,
the affine_shape is the same as normalized_dim by default.
To adapt to different situations, we offer this argument here.
normalized_dim (tuple or list): Which dims to compute mean and variance.
scale (bool): Flag indicates whether to use scale or not.
bias (bool): Flag indicates whether to use scale or not.
We give several examples to show how to specify the arguments.
LayerNorm (https://arxiv.org/abs/1607.06450):
For input shape of (B, *, C) like (B, N, C) or (B, H, W, C),
affine_shape=C, normalized_dim=(-1, ), scale=True, bias=True;
For input shape of (B, C, H, W),
affine_shape=(C, 1, 1), normalized_dim=(1, ), scale=True, bias=True.
Modified LayerNorm (https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418)
that is idental to partial(torch.nn.GroupNorm, num_groups=1):
For input shape of (B, N, C),
affine_shape=C, normalized_dim=(1, 2), scale=True, bias=True;
For input shape of (B, H, W, C),
affine_shape=C, normalized_dim=(1, 2, 3), scale=True, bias=True;
For input shape of (B, C, H, W),
affine_shape=(C, 1, 1), normalized_dim=(1, 2, 3), scale=True, bias=True.
For the several metaformer baslines,
IdentityFormer, RandFormer and PoolFormerV2 utilize Modified LayerNorm without bias (bias=False);
ConvFormer and CAFormer utilizes LayerNorm without bias (bias=False).
"""
def __init__(self, affine_shape=None, normalized_dim=(-1,), scale=True,
bias=True, eps=1e-5):
super().__init__()
self.normalized_dim = normalized_dim
self.use_scale = scale
self.use_bias = bias if isinstance(affine_shape, int):
affine_shape = [affine_shape]
self.weight = self.create_parameter(shape=affine_shape, default_initializer=nn.initializer.Constant(1.0)) if scale else None
self.bias = self.create_parameter(shape=affine_shape, default_initializer=nn.initializer.Constant(0.0)) if bias else None
self.eps = eps def forward(self, x):
c = x - x.mean(self.normalized_dim, keepdim=True)
s = c.pow(2).mean(self.normalized_dim, keepdim=True)
x = c / paddle.sqrt(s + self.eps) if self.use_scale:
x = x * self.weight if self.use_bias:
x = x + self.bias return x
def resize_complex_weight(origin_weight, new_h, new_w):
h, w, num_heads = origin_weight.shape[0:3] # size, w, c, 2
origin_weight = origin_weight.reshape((1, h, w, num_heads * 2)).transpose([0, 3, 1, 2])
new_weight = F.interpolate(
origin_weight,
size=(new_h, new_w),
mode='bicubic',
align_corners=True
).transpose([0, 2, 3, 1]).reshape((new_h, new_w, num_heads, 2)) return new_weight
class DynamicFilter(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, dim, expansion_ratio=2, reweight_expansion_ratio=.25,
act1_layer=StarReLU, act2_layer=nn.Identity,
bias=False, num_filters=4, size=14, weight_resize=False,
**kwargs):
super().__init__()
size = to_2tuple(size)
self.size = size[0]
self.filter_size = size[1] // 2 + 1
self.num_filters = num_filters
self.dim = dim
self.med_channels = int(expansion_ratio * dim)
self.weight_resize = weight_resize
self.pwconv1 = nn.Linear(dim, self.med_channels, bias_attr=bias)
self.act1 = act1_layer()
self.reweight = Mlp(dim, reweight_expansion_ratio, num_filters * self.med_channels)
self.complex_weights = self.create_parameter(shape=(self.size, self.filter_size, num_filters, 2), default_initializer=nn.initializer.TruncatedNormal(std=.02))
self.act2 = act2_layer()
self.pwconv2 = nn.Linear(self.med_channels, dim, bias_attr=bias) def forward(self, x):
B, H, W, _ = x.shape
routeing = self.reweight(x.mean(axis=(1, 2))).reshape((B, self.num_filters, -1))
routeing = F.softmax(routeing, axis=1)
x = self.pwconv1(x)
x = self.act1(x)
x = paddle.fft.rfft2(x, axes=(1, 2), norm='ortho') if self.weight_resize:
complex_weights = resize_complex_weight(self.complex_weights, x.shape[1], x.shape[2]) else:
complex_weights = self.complex_weights
weight = paddle.einsum('bfc,hwfl->bhwcl', routeing, complex_weights)
weight = paddle.as_complex(weight) if self.weight_resize:
weight = weight.reshape((-1, x.shape[1], x.shape[2], self.med_channels)) else:
weight = weight.reshape((-1, self.size, self.filter_size, self.med_channels))
x = x * weight
x = paddle.fft.irfft2(x, s=(H, W), axes=(1, 2), norm='ortho')
x = self.act2(x)
x = self.pwconv2(x) return x
model = DynamicFilter(64, weight_resize=True) paddle.summary(model, (1, 7, 7, 64))
W0620 00:36:11.961606 396 gpu_resources.cc:61] Please NOTE: device: 0, GPU Compute Capability: 7.0, Driver API Version: 11.2, Runtime API Version: 11.2 W0620 00:36:11.971352 396 gpu_resources.cc:91] device: 0, cuDNN Version: 8.2.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Layer (type) Input Shape Output Shape Param #
===========================================================================
Linear-2 [[1, 64]] [1, 16] 1,024
ReLU-6 [[1, 16]] [1, 16] 0
StarReLU-2 [[1, 16]] [1, 16] 2
Dropout-1 [[1, 16]] [1, 16] 0
Linear-3 [[1, 16]] [1, 512] 8,192
Dropout-2 [[1, 512]] [1, 512] 0
Mlp-1 [[1, 64]] [1, 512] 0
Linear-1 [[1, 7, 7, 64]] [1, 7, 7, 128] 8,192
ReLU-5 [[1, 7, 7, 128]] [1, 7, 7, 128] 0
StarReLU-1 [[1, 7, 7, 128]] [1, 7, 7, 128] 2
Identity-1 [[1, 7, 7, 128]] [1, 7, 7, 128] 0
Linear-4 [[1, 7, 7, 128]] [1, 7, 7, 64] 8,192
===========================================================================
Total params: 25,604
Trainable params: 25,604
Non-trainable params: 0
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
Input size (MB): 0.01
Forward/backward pass size (MB): 0.23
Params size (MB): 0.10
Estimated Total Size (MB): 0.34
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
{'total_params': 25604, 'trainable_params': 25604}
class MlpHead(nn.Layer):
""" MLP classification head
"""
def __init__(self, dim, num_classes=1000, mlp_ratio=4, act_layer=SquaredReLU,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm, head_dropout=0., bias=True):
super().__init__()
hidden_features = int(mlp_ratio * dim)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_features, bias_attr=bias)
self.act = act_layer()
self.norm = norm_layer(hidden_features)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, num_classes, bias_attr=bias)
self.head_dropout = nn.Dropout(head_dropout) def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.norm(x)
x = self.head_dropout(x)
x = self.fc2(x) return x
class MetaFormerBlock(nn.Layer):
"""
Implementation of one MetaFormer block.
"""
def __init__(self, dim,
token_mixer=nn.Identity, mlp=Mlp,
norm_layer=nn.LayerNorm,
drop=0., drop_path=0.,
layer_scale_init_value=None, res_scale_init_value=None,
size=14, ):
super().__init__()
self.norm1 = norm_layer(dim)
self.token_mixer = token_mixer(dim=dim, drop=drop, size=size)
self.drop_path2 = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.layer_scale1 = Scale(dim=dim, init_value=layer_scale_init_value) \ if layer_scale_init_value else nn.Identity()
self.res_scale1 = Scale(dim=dim, init_value=res_scale_init_value) \ if res_scale_init_value else nn.Identity()
self.norm2 = norm_layer(dim)
self.mlp = mlp(dim=dim, drop=drop)
self.drop_path2 = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.layer_scale2 = Scale(dim=dim, init_value=layer_scale_init_value) \ if layer_scale_init_value else nn.Identity()
self.res_scale2 = Scale(dim=dim, init_value=res_scale_init_value) \ if res_scale_init_value else nn.Identity() def forward(self, x):
x = self.res_scale1(x) + \
self.layer_scale1(
self.drop_path2(
self.token_mixer(self.norm1(x))
)
)
x = self.res_scale2(x) + \
self.layer_scale2(
self.drop_path2(
self.mlp(self.norm2(x))
)
) return x
DOWNSAMPLE_LAYERS_FOUR_STAGES = [partial(Downsampling,
kernel_size=7, stride=4, padding=2,
post_norm=partial(LayerNormGeneral, bias=False,
eps=1e-6)
)] + \
[partial(Downsampling,
kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1,
pre_norm=partial(LayerNormGeneral, bias=False,
eps=1e-6), pre_permute=True
)] * 3class MetaFormer(nn.Layer):
r""" MetaFormer
A PyTorch impl of : `MetaFormer Baselines for Vision` -
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13452
Args:
in_chans (int): Number of input image channels. Default: 3.
num_classes (int): Number of classes for classification head. Default: 1000.
depths (list or tuple): Number of blocks at each stage. Default: [2, 2, 6, 2].
dims (int): Feature dimension at each stage. Default: [64, 128, 320, 512].
downsample_layers: (list or tuple): Downsampling layers before each stage.
token_mixers (list, tuple or token_fcn): Token mixer for each stage. Default: nn.Identity.
mlps (list, tuple or mlp_fcn): Mlp for each stage. Default: Mlp.
norm_layers (list, tuple or norm_fcn): Norm layers for each stage. Default: partial(LayerNormGeneral, eps=1e-6, bias=False).
drop_path_rate (float): Stochastic depth rate. Default: 0.
head_dropout (float): dropout for MLP classifier. Default: 0.
layer_scale_init_values (list, tuple, float or None): Init value for Layer Scale. Default: None.
None means not use the layer scale. Form: https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.17239.
res_scale_init_values (list, tuple, float or None): Init value for Layer Scale. Default: [None, None, 1.0, 1.0].
None means not use the layer scale. From: https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.09456.
fork_feat (bool): whether output features of the 4 stages, for dense prediction
output_norm: norm before classifier head. Default: partial(nn.LayerNorm, eps=1e-6).
head_fn: classification head. Default: nn.Linear.
"""
def __init__(self, in_chans=3, num_classes=1000,
depths=[2, 2, 6, 2],
dims=[64, 128, 320, 512],
downsample_layers=DOWNSAMPLE_LAYERS_FOUR_STAGES,
token_mixers=nn.Identity,
mlps=Mlp,
norm_layers=partial(LayerNormGeneral, eps=1e-6, bias=False),
drop_path_rate=0.,
head_dropout=0.0,
layer_scale_init_values=None,
res_scale_init_values=[None, None, 1.0, 1.0],
output_norm=partial(nn.LayerNorm, epsilon=1e-6),
head_fn=nn.Linear,
input_size=(3, 224, 224),
**kwargs, ):
super().__init__()
self.num_classes = num_classes if not isinstance(depths, (list, tuple)):
depths = [depths] # it means the model has only one stage
if not isinstance(dims, (list, tuple)):
dims = [dims]
num_stage = len(depths)
self.num_stage = num_stage if not isinstance(downsample_layers, (list, tuple)):
downsample_layers = [downsample_layers] * num_stage
down_dims = [in_chans] + dims
self.downsample_layers = nn.LayerList(
[downsample_layers[i](down_dims[i], down_dims[i + 1]) for i in
range(num_stage)]
) if not isinstance(token_mixers, (list, tuple)):
token_mixers = [token_mixers] * num_stage if not isinstance(mlps, (list, tuple)):
mlps = [mlps] * num_stage if not isinstance(norm_layers, (list, tuple)):
norm_layers = [norm_layers] * num_stage
dp_rates = [x.item() for x in paddle.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))] if not isinstance(layer_scale_init_values, (list, tuple)):
layer_scale_init_values = [layer_scale_init_values] * num_stage if not isinstance(res_scale_init_values, (list, tuple)):
res_scale_init_values = [res_scale_init_values] * num_stage
self.stages = nn.LayerList() # each stage consists of multiple metaformer blocks
cur = 0
for i in range(num_stage):
stage = nn.Sequential(
*[MetaFormerBlock(dim=dims[i],
token_mixer=token_mixers[i],
mlp=mlps[i],
norm_layer=norm_layers[i],
drop_path=dp_rates[cur + j],
layer_scale_init_value=layer_scale_init_values[i],
res_scale_init_value=res_scale_init_values[i],
size=(input_size[1] // (2 ** (i + 2)),
input_size[2] // (2 ** (i + 2))),
) for j in range(depths[i])]
)
self.stages.append(stage)
cur += depths[i]
self.norm = output_norm(dims[-1]) if head_dropout > 0.0:
self.head = head_fn(dims[-1], num_classes, head_dropout=head_dropout) else:
self.head = head_fn(dims[-1], num_classes)
self.apply(self._init_weights) def _init_weights(self, m):
tn = nn.initializer.TruncatedNormal(std=.02)
zero = nn.initializer.Constant(0.0) if isinstance(m, (nn.Conv2D, nn.Linear)):
tn(m.weight) if m.bias is not None:
zero(m.bias) def forward_features(self, x):
outs = [] for i in range(self.num_stage):
x = self.downsample_layers[i](x)
x = self.stages[i](x) return self.norm(x.mean([1, 2])) # (B, H, W, C) -> (B, C)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.forward_features(x)
x = self.head(x) return x
def dfformer_s18(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model = MetaFormer(
depths=[3, 3, 9, 3],
dims=[64, 128, 320, 512],
token_mixers=DynamicFilter,
head_fn=MlpHead,
input_size=(3, 224, 224),
**kwargs) return modeldef dfformer_s36(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model = MetaFormer(
depths=[3, 12, 18, 3],
dims=[64, 128, 320, 512],
token_mixers=DynamicFilter,
head_fn=MlpHead,
input_size=(3, 224, 224),
**kwargs) return modeldef dfformer_m36(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model = MetaFormer(
depths=[3, 12, 18, 3],
dims=[96, 192, 384, 576],
token_mixers=DynamicFilter,
head_fn=MlpHead,
input_size=(3, 224, 224),
**kwargs) return modeldef dfformer_b36(pretrained=False, **kwargs):
model = MetaFormer(
depths=[3, 12, 18, 3],
dims=[128, 256, 512, 768],
token_mixers=DynamicFilter,
head_fn=MlpHead,
input_size=(3, 224, 224),
**kwargs) return model
2.3.4 模型的参数
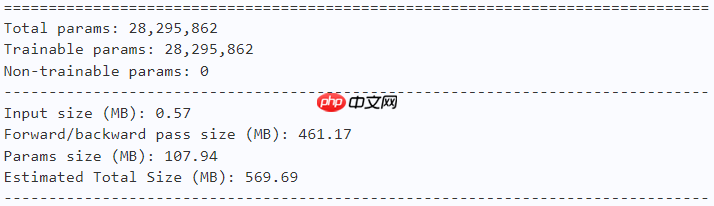
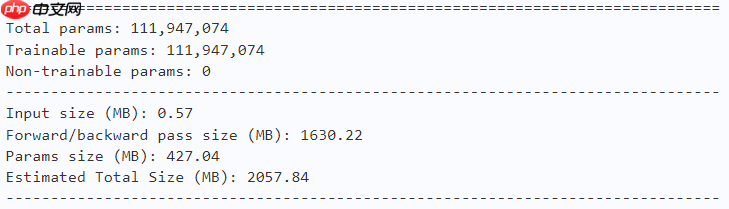
model = dfformer_s18(num_classes=10) paddle.summary(model, (1, 3, 224, 224))
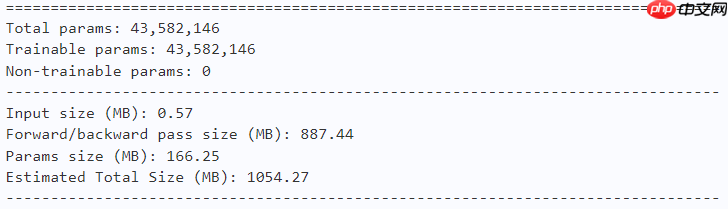
model = dfformer_s36(num_classes=10) paddle.summary(model, (1, 3, 224, 224))
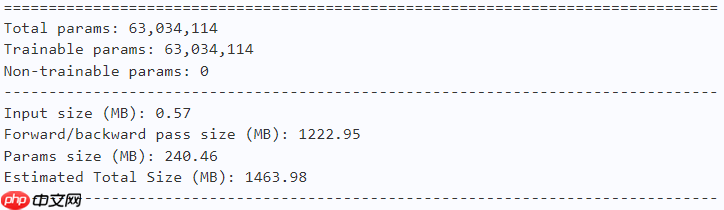
model = dfformer_m36(num_classes=10) paddle.summary(model, (1, 3, 224, 224))
model = dfformer_b36(num_classes=10) paddle.summary(model, (1, 3, 224, 224))
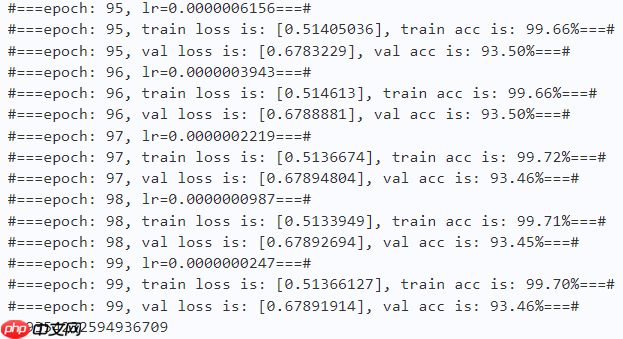
2.4 训练
learning_rate = 0.0001n_epochs = 100paddle.seed(42) np.random.seed(42)
work_path = 'work/model'# DFFormer-S18model = dfformer_s18(num_classes=10)
criterion = LabelSmoothingCrossEntropy()
scheduler = paddle.optimizer.lr.CosineAnnealingDecay(learning_rate=learning_rate, T_max=50000 // batch_size * n_epochs, verbose=False)
optimizer = paddle.optimizer.Adam(parameters=model.parameters(), learning_rate=scheduler, weight_decay=1e-5)
gate = 0.0threshold = 0.0best_acc = 0.0val_acc = 0.0loss_record = {'train': {'loss': [], 'iter': []}, 'val': {'loss': [], 'iter': []}} # for recording lossacc_record = {'train': {'acc': [], 'iter': []}, 'val': {'acc': [], 'iter': []}} # for recording accuracyloss_iter = 0acc_iter = 0for epoch in range(n_epochs): # ---------- Training ----------
model.train()
train_num = 0.0
train_loss = 0.0
val_num = 0.0
val_loss = 0.0
accuracy_manager = paddle.metric.Accuracy()
val_accuracy_manager = paddle.metric.Accuracy() print("#===epoch: {}, lr={:.10f}===#".format(epoch, optimizer.get_lr())) for batch_id, data in enumerate(train_loader):
x_data, y_data = data
labels = paddle.unsqueeze(y_data, axis=1)
logits = model(x_data)
loss = criterion(logits, y_data)
acc = accuracy_manager.compute(logits, labels)
accuracy_manager.update(acc) if batch_id % 10 == 0:
loss_record['train']['loss'].append(loss.numpy())
loss_record['train']['iter'].append(loss_iter)
loss_iter += 1
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
optimizer.clear_grad()
train_loss += loss
train_num += len(y_data)
total_train_loss = (train_loss / train_num) * batch_size
train_acc = accuracy_manager.accumulate()
acc_record['train']['acc'].append(train_acc)
acc_record['train']['iter'].append(acc_iter)
acc_iter += 1
# Print the information.
print("#===epoch: {}, train loss is: {}, train acc is: {:2.2f}%===#".format(epoch, total_train_loss.numpy(), train_acc*100)) # ---------- Validation ----------
model.eval() for batch_id, data in enumerate(val_loader):
x_data, y_data = data
labels = paddle.unsqueeze(y_data, axis=1) with paddle.no_grad():
logits = model(x_data)
loss = criterion(logits, y_data)
acc = val_accuracy_manager.compute(logits, labels)
val_accuracy_manager.update(acc)
val_loss += loss
val_num += len(y_data)
total_val_loss = (val_loss / val_num) * batch_size
loss_record['val']['loss'].append(total_val_loss.numpy())
loss_record['val']['iter'].append(loss_iter)
val_acc = val_accuracy_manager.accumulate()
acc_record['val']['acc'].append(val_acc)
acc_record['val']['iter'].append(acc_iter) print("#===epoch: {}, val loss is: {}, val acc is: {:2.2f}%===#".format(epoch, total_val_loss.numpy(), val_acc*100)) # ===================save====================
if val_acc > best_acc:
best_acc = val_acc
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(work_path, 'best_model.pdparams'))
paddle.save(optimizer.state_dict(), os.path.join(work_path, 'best_optimizer.pdopt'))print(best_acc)
paddle.save(model.state_dict(), os.path.join(work_path, 'final_model.pdparams'))
paddle.save(optimizer.state_dict(), os.path.join(work_path, 'final_optimizer.pdopt'))
2.5 结果分析
def plot_learning_curve(record, title='loss', ylabel='CE Loss'):
''' Plot learning curve of your CNN '''
maxtrain = max(map(float, record['train'][title]))
maxval = max(map(float, record['val'][title]))
ymax = max(maxtrain, maxval) * 1.1
mintrain = min(map(float, record['train'][title]))
minval = min(map(float, record['val'][title]))
ymin = min(mintrain, minval) * 0.9
total_steps = len(record['train'][title])
x_1 = list(map(int, record['train']['iter']))
x_2 = list(map(int, record['val']['iter']))
figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(x_1, record['train'][title], c='tab:red', label='train')
plt.plot(x_2, record['val'][title], c='tab:cyan', label='val')
plt.ylim(ymin, ymax)
plt.xlabel('Training steps')
plt.ylabel(ylabel)
plt.title('Learning curve of {}'.format(title))
plt.legend()
plt.show()
plot_learning_curve(loss_record, title='loss', ylabel='CE Loss')
<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>
plot_learning_curve(acc_record, title='acc', ylabel='Accuracy')
<Figure size 1000x600 with 1 Axes>
import time
work_path = 'work/model'model = dfformer_s18(num_classes=10)
model_state_dict = paddle.load(os.path.join(work_path, 'best_model.pdparams'))
model.set_state_dict(model_state_dict)
model.eval()
aa = time.time()for batch_id, data in enumerate(val_loader):
x_data, y_data = data
labels = paddle.unsqueeze(y_data, axis=1) with paddle.no_grad():
logits = model(x_data)
bb = time.time()print("Throughout:{}".format(int(len(val_dataset)//(bb - aa))))
Throughout:458
def get_cifar10_labels(labels):
"""返回CIFAR10数据集的文本标签。"""
text_labels = [ 'airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'] return [text_labels[int(i)] for i in labels]
def show_images(imgs, num_rows, num_cols, pred=None, gt=None, scale=1.5):
"""Plot a list of images."""
figsize = (num_cols * scale, num_rows * scale)
_, axes = plt.subplots(num_rows, num_cols, figsize=figsize)
axes = axes.flatten() for i, (ax, img) in enumerate(zip(axes, imgs)): if paddle.is_tensor(img):
ax.imshow(img.numpy()) else:
ax.imshow(img)
ax.axes.get_xaxis().set_visible(False)
ax.axes.get_yaxis().set_visible(False) if pred or gt:
ax.set_title("pt: " + pred[i] + "\ngt: " + gt[i]) return axes
work_path = 'work/model'X, y = next(iter(DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=18))) model = dfformer_s18(num_classes=10) model_state_dict = paddle.load(os.path.join(work_path, 'best_model.pdparams')) model.set_state_dict(model_state_dict) model.eval() logits = model(X) y_pred = paddle.argmax(logits, -1) X = paddle.transpose(X, [0, 2, 3, 1]) axes = show_images(X.reshape((18, 224, 224, 3)), 1, 18, pred=get_cifar10_labels(y_pred), gt=get_cifar10_labels(y)) plt.show()
Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers). Clipping input data to the valid range for imshow with RGB data ([0..1] for floats or [0..255] for integers).
<Figure size 2700x150 with 18 Axes>






























