let's delve into the apache spark architecture, providing a high-level overview and discussing some key software components in detail.
High-Level Overview Apache Spark's application architecture is composed of several crucial components that work together to process data in a distributed environment. Understanding these components is essential for grasping how Spark functions. The key components include:
- Driver Program
- Master Node
- Worker Node
- Executor
- Tasks
- SparkContext
- SQL Context
- Spark Session
Here's an overview of how these components integrate within the overall architecture:
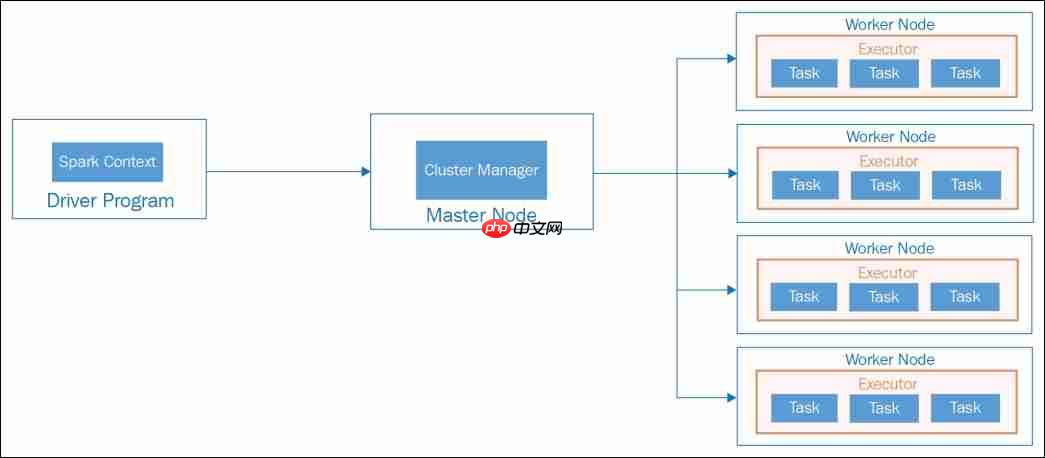 Apache Spark application architecture - Standalone mode
Apache Spark application architecture - Standalone mode
Driver Program The Driver Program serves as the primary component of a Spark application. The machine hosting the Spark application process, which initializes SparkContext and Spark Session, is referred to as the Driver Node, and the running process is known as the Driver Process. This program interacts with the Cluster Manager to allocate tasks to executors.
Cluster Manager As the name suggests, a Cluster Manager oversees a cluster. Spark is compatible with various cluster managers such as YARN, Mesos, and a Standalone cluster manager. In a standalone setup, there are two continuously running daemons: one on the master node and one on each worker node. Further details on cluster managers and deployment models will be covered in Chapter 8, Operating in Clustered Mode.
Worker If you're familiar with Hadoop, you'll recognize that a Worker Node is akin to a slave node. These nodes are where the actual computational work occurs within Spark executors. They report their available resources back to the master node. Typically, each node in a Spark cluster, except the master, runs a worker process. Usually, one Spark worker daemon is initiated per worker node, which then launches and oversees executors for the applications.
Executors The master node allocates resources and utilizes workers across the cluster to instantiate Executors for the driver. These executors are employed by the driver to execute tasks. Executors are initiated only when a job begins on a worker node. Each application maintains its own set of executor processes, which can remain active throughout the application's lifecycle and execute tasks across multiple threads. This approach ensures application isolation and prevents data sharing between different applications. Executors are responsible for task execution and managing data in memory or on disk.
Tasks A task represents a unit of work dispatched to an executor. It is essentially a command sent from the Driver Program to an executor, serialized as a Function object. The executor deserializes this command (which is part of your previously loaded JAR) and executes it on a specific data partition.
A partition is a logical division of data spread across a Spark cluster. Spark typically reads data from a distributed storage system and partitions it to facilitate parallel processing across the cluster. For instance, when reading from HDFS, a partition is created for each HDFS partition. Partitions are crucial because Spark executes one task per partition. Consequently, the number of partitions is significant. Spark automatically sets the number of partitions unless manually specified, e.g., sc.parallelize(data, numPartitions).

开发语言:java,支持数据库:Mysql 5,系统架构:J2EE,操作系统:linux/Windows1. 引言 32. 系统的结构 32.1 系统概述 33. 功能模块设计说明 43.1 商品管理 43.1.1 添加商品功能模块 53.1.2 商品列表功能模块 83.1.3 商品关联功能模块 93.
SparkContext
SparkContext serves as the entry point for a Spark session. It connects you to the Spark cluster and enables the creation of RDDs, accumulators, and broadcast variables on that cluster. Ideally, only one SparkContext should be active per JVM. Therefore, you must call stop() on the active SparkContext before initiating a new one. In local mode, when starting a Python or Scala shell, a SparkContext object is automatically created, and the variable sc references this SparkContext object, allowing you to create RDDs from text files without explicitly initializing it.
/**
* Read a text file from HDFS, a local file system (available on all nodes), or any
* Hadoop-supported file system URI, and return it as an RDD of Strings.
* The text files must be encoded as UTF-8.
*
* @param path path to the text file on a supported file system
* @param minPartitions suggested minimum number of partitions for the resulting RDD
* @return RDD of lines of the text file
*/
def textFile(
path: String,
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[String] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
hadoopFile(path, classOf[TextInputFormat], classOf[LongWritable], classOf[Text],
minPartitions).map(pair => pair._2.toString).setName(path)
}
<p>/** Get an RDD for a Hadoop file with an arbitrary InputFormat</p><ul><li></li><li>@note Because Hadoop's RecordReader class re-uses the same Writable object for each </li><li>record, directly caching the returned RDD or directly passing it to an aggregation or shuffle </li><li>operation will create many references to the same object.</li><li>If you plan to directly cache, sort, or aggregate Hadoop writable objects, you should first </li><li>copy them using a <code>map function.</li><li>@param path directory to the input data files, the path can be comma separated paths </li><li>as a list of inputs</li><li>@param inputFormatClass storage format of the data to be read</li><li>@param keyClass <code>Class</code> of the key associated with the <code>inputFormatClass</code> parameter</li><li>@param valueClass <code>Class</code> of the value associated with the <code>inputFormatClass</code> parameter</li><li>@param minPartitions suggested minimum number of partitions for the resulting RDD</li><li>@return RDD of tuples of key and corresponding value
*/
def hadoopFile[K, V](
path: String,
inputFormatClass: Class[_ <: InputFormat[K, V]],
keyClass: Class[K],
valueClass: Class[V],
minPartitions: Int = defaultMinPartitions): RDD[(K, V)] = withScope {
assertNotStopped()
val confBroadcast = broadcast(new SerializableConfiguration(hadoopConfiguration))
val setInputPathsFunc = (jobConf: JobConf) => FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(jobConf, path)
new HadoopRDD(
this,
confBroadcast,
Some(setInputPathsFunc),
inputFormatClass,
keyClass,
valueClass,
minPartitions).setName(path)
}</code>Spark Session The Spark Session is the entry point for programming with Spark using the dataset and DataFrame API.
For more in-depth information, you can refer to the following resource: Apache Spark Architecture.





























