您经常需要假数据来进行测试。当然,您可以在测试中使用一些示例数据。但是,如果您需要数百条甚至数千条测试数据怎么办?那么创建和维护就会变得乏味。有时,您只需要程序中类的假版本,但您希望它是行为类似于真实类的真实数据。工厂和假货让这一切成为可能。
在本文中,我们将使用 python 中的 factory-boy 包来生成假数据。
请确保使用命令 pip installfactory-boy==2.12.0 安装正确版本的factory-boy
让我们尝试使用 factory boy 生成一些假数据
import factory #import factory-boy
name = factory.faker('name') #create faker object with 'name' provider
for _ in range(5):
print(name.generate()) #generate and print 5 unique names
结果:
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;

factory.faker() 接受一个称为provider 的参数,用于生成数据类型,例如“name”provider 将用于生成名称,“email”provider 将用于生成电子邮件等。
让我们尝试使用更多的提供商
import factory #import factory-boy
name = factory.faker('name') #create faker object with 'name' provider
country = factory.faker('country') #create faker object with 'country' provider
email = factory.faker('email') #create faker object with 'email' provider
for _ in range(3):
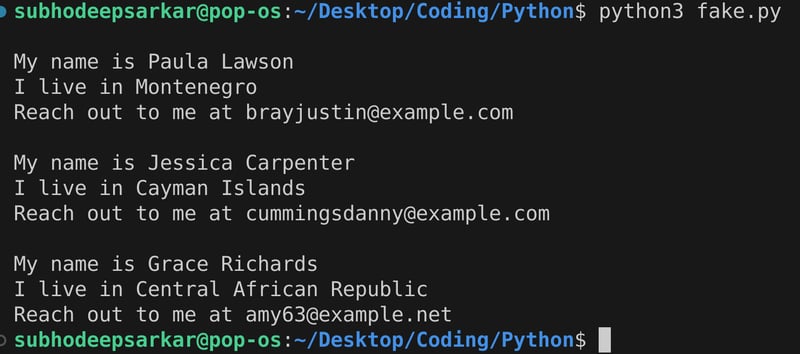
print(f'''
my name is {name.generate()}
i live in {country.generate()}
reach out to me at {email.generate()}''')
结果:
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;
除了faker类之外,factory-boy还有一个模块fuzzy,我们来看看它是如何工作的
import factory #import factory-boy module
import factory.fuzzy #import fuzzy module
name = factory.faker('name') #create faker object with 'name' provider
gender = factory.fuzzy.fuzzychoice(choices=['girl','boy']) #create fuzzychoice object which selects from the given options
grade = factory.fuzzy.fuzzyfloat(30,80) #create fuzzyfloat object which generates a random float number between the lower and upper limit
age = factory.fuzzy.fuzzyinteger(12,18) #create fuzzyinteger object which generates a random float numbeer between the lower and upper limit
for _ in range(3):
print(f'''my name is {name.generate()}, i am a {gender.fuzz()}
i got a grade of {grade.fuzz():.2f}% and my age is {age.fuzz()}
''')
结果:
立即学习“Python免费学习笔记(深入)”;

要了解有关模糊模块中不同类的更多信息以及 faker 提供者的各种选项,请访问:https://factoryboy.readthedocs.io/en/stable
现在我们知道了 factory-boy 如何模仿数据,让我们尝试模仿通常用于为 flask、django 等应用程序创建数据库表的数据模型。
对于这个项目,创建一个requirements.txt并粘贴以下内容,然后使用pip3 install -rrequirements.txt安装所有必需的包
# pin dependancies that might cause breakage werkzeug==2.1.2 sqlalchemy==1.4.46 # dependencies for this project flask==2.1.2 flask-sqlalchemy==2.5.1 # testing dependencies nose==1.3.7 pinocchio==0.4.3 coverage==6.3.2 factory-boy==2.12.0 pylint==2.14.0
由于我们将使用 nosetest 运行单元测试,请查看我之前的文章 - “使用 unittest 和 nose 在 python 中进行测试驱动开发” (https://dev.to/h4ck3rd33p/test-driven-development-in-python-使用-unittest-and-nosetest-24ck)
创建一个用于nosetests配置的setup.cfg文件并粘贴以下内容
[nosetests] verbosity=2 with-spec=1 spec-color=1 with-coverage=1 cover-erase=1 cover-package=models [coverage:report] show_missing = true
现在创建两个文件夹模型,其中包含 account.py 中的数据模型和 __init__.py 中的基本设置,以及包含工厂模型的测试,该工厂模型将模仿factories.py中的实际模型以及用于测试的相关单元测试test_account.py 中的应用程序.
最终你的文件夹结构应该如下所示:
.
├── models
│ ├── account.py
│ └── __init__.py
├── requirements.txt
├── setup.cfg
└── tests
├── factories.py
└── test_account.py
2 directories, 6 files
假设我们需要测试一个处理客户帐户的数据模型。我们将从创建这个数据模型开始。我们将使用一种名为 sqlalchemy 的流行对象关系映射器,因此我们创建 sqlalchemy 类的数据库实例。现在我们构建我们的模型。我们创建一个名为 accounts 的类,它继承自 sqlalchemy 的基本模型。现在我们可以添加列,这些列将表示为类变量。我们添加一个id。它将作为非信息承载键,因此我们将 id 标记为主键。我们将名称添加为字符串,将电子邮件字段添加为字符串。我们还添加电话号码作为字符串。我们将该电话号码设置为可选,因此我们将 nullable 设置为 true。让我们添加一个布尔字段来确定该帐户是否被禁用,并将默认值设置为 false。最后,我们将添加一个日期连接列作为 datetime 并将其设置为可选。
模型 > __init__.py
""" data models """ from flask import flask from flask_sqlalchemy import sqlalchemy app = flask(__name__) app.config['sqlalchemy_track_modifications'] = false app.config['sqlalchemy_database_uri'] = 'sqlite:///test.db' db = sqlalchemy(app)
模型 > account.py
"""
account class
"""
import logging
from sqlalchemy.sql import func
from models import db
logger = logging.getlogger()
class datavalidationerror(exception):
"""used for an data validation errors when deserializing"""
class account(db.model):
""" class that represents an account """
id = db.column(db.integer, primary_key=true)
name = db.column(db.string(64))
email = db.column(db.string(64))
phone_number = db.column(db.string(32), nullable=true)
disabled = db.column(db.boolean(), nullable=false, default=false)
date_joined = db.column(db.date, nullable=false, server_default=func.now())
def __repr__(self):
return '<account %r>' % self.name
def to_dict(self) -> dict:
"""serializes the class as a dictionary"""
return {c.name: getattr(self, c.name) for c in self.__table__.columns}
def from_dict(self, data: dict) -> none:
"""sets attributes from a dictionary"""
for key, value in data.items():
setattr(self, key, value)
def create(self):
"""creates a account to the database"""
logger.info("creating %s", self.name)
db.session.add(self)
db.session.commit()
def update(self):
"""updates a account to the database"""
logger.info("saving %s", self.name)
if not self.id:
raise datavalidationerror("update called with empty id field")
db.session.commit()
def delete(self):
"""removes a account from the data store"""
logger.info("deleting %s", self.name)
db.session.delete(self)
db.session.commit()
##################################################
# class methods
##################################################
@classmethod
def all(cls) -> list:
"""returns all of the accounts in the database"""
logger.info("processing all accounts")
return cls.query.all()
@classmethod
def find(cls, account_id: int):
"""finds a account by it's id
:param account_id: the id of the account to find
:type account_id: int
:return: an instance with the account_id, or none if not found
:rtype: account
"""
logger.info("processing lookup for id %s ...", account_id)
return cls.query.get(account_id)
现在让我们创建模仿原始 account 类的假类。我们将其命名为 accountfactory。还创建一个内部类 meta 并创建一个属性模型并将其设置为 account,这将使 factory-boy 确切地知道它必须模仿哪个数据类,因此 accountfactory 现在将自动拥有 account 类具有的所有方法。
测试 > 工厂.py
"""
accountfactory class using factoryboy
"""
import factory
from datetime import date
from factory.fuzzy import fuzzychoice, fuzzydate
from models.account import account
class accountfactory(factory.factory):
""" creates fake accounts """
class meta:
model = account
id = factory.sequence(lambda n: n)
name = factory.faker("name")
email = factory.faker("email")
phone_number = factory.faker("phone_number")
disabled = fuzzychoice(choices=[true, false])
date_joined = fuzzydate(date(2008, 1, 1))
id = factory.sequence(lambda n: n) 将生成连续的数字序列 0,1,2...
现在让我们编写单元测试来测试我们的 accountfactory
测试装置:这些是在运行测试用例之前和之后设置系统状态的方法。
setupclass(cls):这用于在运行类中的任何测试用例之前设置系统状态。在我们的示例中,它正在创建数据库和表。
teardownclass(cls):用于在运行当前类中的所有测试用例后清理系统。在我们的示例中,它删除所有剩余的测试数据并断开与数据库的连接。
setup(self):这用于在运行单个测试用例之前设置系统。在我们的示例中,它正在删除数据并保存它。
teardown(self):这用于在运行单个测试用例后重置系统状态。在我们的示例中,它正在关闭当前数据库会话。
setupall:这用于在进入任何类之前设置系统状态。 我们在示例中没有使用这个
teardownall:这用于在完成所有类后重置系统状态。 我们在示例中没有使用这个
测试 > test_account.py
"""
Test Cases TestAccountModel
"""
from random import randrange
from unittest import TestCase
from models import db
from models.account import Account, DataValidationError
from factories import AccountFactory
class TestAccountModel(TestCase):
"""Test Account Model"""
@classmethod
def setUpClass(cls): #Runs before running any unit test
""" Create table """
db.create_all() # make our sqlalchemy tables
@classmethod
def tearDownClass(cls): #Runs after running all the tests
"""Delete test data and Disconnext from database"""
db.session.query(Account).delete()
db.session.close()
def setUp(self): #Runs before running every individual test
"""Drop the table"""
db.session.query(Account).delete()
db.session.commit()
def tearDown(self): #Runs after ruunning every individual test
"""Remove the session"""
db.session.remove()
######################################################################
# T E S T C A S E S
######################################################################
def test_create_all_accounts(self):
""" Test creating multiple Accounts """
for _ in range(10):
account = AccountFactory()
account.create()
self.assertEqual(len(Account.all()), 10)
def test_create_an_account(self):
""" Test Account creation using known data """
account = AccountFactory()
account.create()
self.assertEqual(len(Account.all()), 1)
def test_repr(self):
"""Test the representation of an account"""
account = Account()
account.name = "Foo"
self.assertEqual(str(account), "<Account 'Foo'>")
def test_to_dict(self):
""" Test account to dict """
account = AccountFactory()
result = account.to_dict()
self.assertEqual(account.name, result["name"])
self.assertEqual(account.email, result["email"])
self.assertEqual(account.phone_number, result["phone_number"])
self.assertEqual(account.disabled, result["disabled"])
self.assertEqual(account.date_joined, result["date_joined"])
def test_from_dict(self):
""" Test account from dict """
data = AccountFactory().to_dict()
account = Account()
account.from_dict(data)
self.assertEqual(account.name, data["name"])
self.assertEqual(account.email, data["email"])
self.assertEqual(account.phone_number, data["phone_number"])
self.assertEqual(account.disabled, data["disabled"])
def test_update_an_account(self):
""" Test Account update using known data """
account = AccountFactory()
account.create()
self.assertIsNotNone(account.id)
account.name = "Rumpelstiltskin"
account.update()
found = Account.find(account.id)
self.assertEqual(found.name, account.name)
self.assertIsNotNone(account.id)
account.name = "Rumpelstiltskin"
account.update()
found = Account.find(account.id)
self.assertEqual(found.name, account.name)
def test_invalid_id_on_update(self):
""" Test invalid ID update """
account = AccountFactory()
account.id = None
self.assertRaises(DataValidationError, account.update)
def test_delete_an_account(self):
""" Test Account update using known data """
account = AccountFactory()
account.create()
self.assertEqual(len(Account.all()), 1)
account.delete()
self.assertEqual(len(Account.all()), 0)
阅读评论以了解有关测试用例的更多信息。现在让我们运行鼻子测试
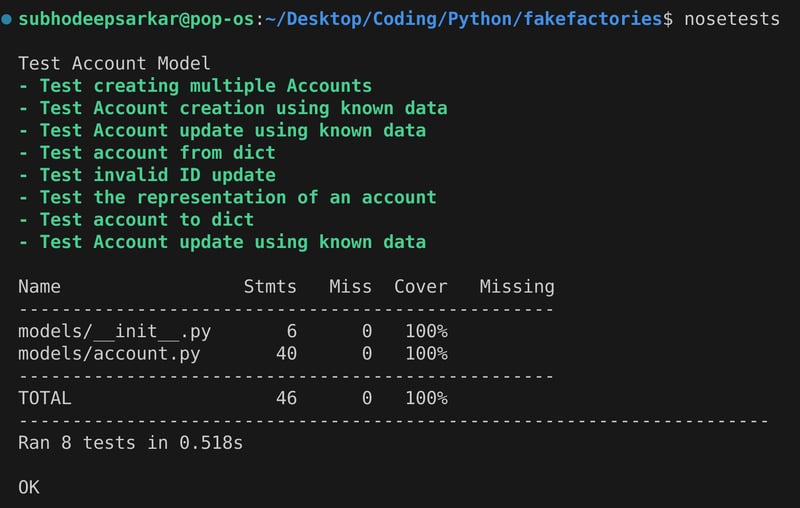
恭喜!所有测试用例都已通过,因此我们可以得出结论,我们的 accountfactory 与 account 类完全相同,并且已使用 factory-boy 使用虚假数据测试了应用程序!






























