首先我来大概的介绍一下location的种类和匹配规则,以nginx wiki的例子做说明:
location = / {
# matches the query / only.
[ configuration a ]
}
location / {
# matches any query, since all queries begin with /, but regular
# expressions and any longer conventional blocks will be
# matched first.
[ configuration b ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
# matches any query beginning with /images/ and halts searching,
# so regular expressions will not be checked.
[ configuration c ]
}
location ~* \.(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
# matches any request ending in gif, jpg, or jpeg. however, all
# requests to the /images/ directory will be handled by
# configuration c.
[ configuration d ]
}
location @named {
# such locations are not used during normal processing of requests,
# they are intended only to process internally redirected requests (for example error_page, try_files).
[ configuration e ]
}可以看到上面的例子中有5种不同类型的location,其中第4个带 “~” 号前缀的为需要正则匹配的location,nginx在进行url解析时对这5种不同类型的location具有不同的优先级规则,大致的规则如下:
1,字符串精确匹配到一个带 “=” 号前缀的location,则停止,且使用这个location的配置;
2,字符串匹配剩下的非正则和非特殊location,如果匹配到某个带 "^~" 前缀的location,则停止;
3,正则匹配,匹配顺序为location在配置文件中出现的顺序。如果匹配到某个正则location,则停止,并使用这个location的配置;否则,使用步骤2中得到的具有最大字符串匹配的location配置。
例如,对下面的请求有:
1, / -> 精确匹配到第1个location,匹配停止,使用configuration a
2,/some/other/url -> 首先前缀部分字符串匹配到了第2个location,然后进行正则匹配,显然没有匹配上,则使用第2个location的配置configurationb
3,/images /1.jpg -> 首先前缀部分字符串匹配到了第2个location,但是接着对第3个location也前缀匹配上了,而且这时已经是配置文件里面对这个url的最大字符串匹配了,并且location带有 "^~" 前缀,则不再进行正则匹配,最终使用configuration c
4,/some/other/path/to/1.jpg -> 首先前缀部分同样字符串匹配到了第2个location,然后进行正则匹配,这时正则匹配成功,则使用congifuration d
nginx的url匹配规则实际上有点不妥,大部分情况下一个url必须先进行字符串匹配,然后再做正则匹配,但是实际上如果先做正则匹配,没有匹配上再 做字符串匹配,在很多情况下可以节省掉做字符串匹配的时间。不管怎样,先来看一下nginx源码里面的实现,在介绍匹配location过程之前,先来介 绍一下nginx里面对location的组织方式,实际上在配置解析阶段,nginx将字符串匹配的location和正则匹配的location分别 存储在http core模块的loc配置ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t结构的下面2个字段:
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *static_locations; (ngx_pcre) ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **regex_locations; if
从这2个字段的类型可以看出,字符串匹配的location被组织成了一个location tree,而正则匹配的location只是一个数组,
location tree和regex_locations数组建立过程在ngx_http_block中:
/* create location trees */
for (s = 0; s < cmcf->servers.nelts; s++) {
clcf = cscfp[s]->ctx->loc_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, cscfp[s], clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_conf_error;
}
if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_conf_error;
}
} 经过配置的读取之后,所有server都被保存在http core模块的main配置中的servers数组中,而每个server里面的location都被按配置中出现的顺序保存在http core模块的loc配置的locations队列中,上面的代码中先对每个server的location进行排序和分类处理,这一步发生在 ngx_http_init_location()函数中:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_init_locations(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf,
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
{
...
locations = pclcf->locations;
...
/* 按照类型排序location,排序完后的队列: (exact_match 或 inclusive) (排序好的,如果某个exact_match名字和inclusive location相同,exact_match排在前面)
| regex(未排序)| named(排序好的) | noname(未排序)*/
ngx_queue_sort(locations, ngx_http_cmp_locations);
named = null;
n = 0;
#if (ngx_pcre)
regex = null;
r = 0;
#endif
for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
/* 由于可能存在nested location,也就是location里面嵌套的location,这里需要递归的处理一下当前location下面的nested location */
if (ngx_http_init_locations(cf, null, clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_error;
}
#if (ngx_pcre)
if (clcf->regex) {
r++;
if (regex == null) {
regex = q;
}
continue;
}
#endif
if (clcf->named) {
n++;
if (named == null) {
named = q;
}
continue;
}
if (clcf->noname) {
break;
}
}
if (q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations)) {
ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
}
/* 如果有named location,将它们保存在所属server的named_locations数组中 */
if (named) {
clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
(n + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
if (clcfp == null) {
return ngx_error;
}
cscf->named_locations = clcfp;
for (q = named;
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
*(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
}
*clcfp = null;
ngx_queue_split(locations, named, &tail);
}
#if (ngx_pcre)
/* 如果有正则匹配location,将它们保存在所属server的http core模块的loc配置的regex_locations 数组中,
这里和named location保存位置不同的原因是由于named location只能存在server里面,而regex location可以作为nested location */
if (regex) {
clcfp = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
(r + 1) * sizeof(ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t **));
if (clcfp == null) {
return ngx_error;
}
pclcf->regex_locations = clcfp;
for (q = regex;
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
*(clcfp++) = lq->exact;
}
*clcfp = null;
ngx_queue_split(locations, regex, &tail);
}
#endif
return ngx_ok;
}
上面的步骤将正则匹配的location保存好了,location tree的建立在ngx_http_init_static_location_trees中进行:
static ngx_int_t
ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(ngx_conf_t *cf,
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *pclcf)
{
ngx_queue_t *q, *locations;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
ngx_http_location_queue_t *lq;
locations = pclcf->locations;
if (locations == null) {
return ngx_ok;
}
if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
return ngx_ok;
}
/* 这里也是由于nested location,需要递归一下 */
for (q = ngx_queue_head(locations);
q != ngx_queue_sentinel(locations);
q = ngx_queue_next(q))
{
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
clcf = lq->exact ? lq->exact : lq->inclusive;
if (ngx_http_init_static_location_trees(cf, clcf) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_error;
}
}
/* join队列中名字相同的inclusive和exact类型location,也就是如果某个exact_match的location名字和普通字符串匹配的location名字相同的话,
就将它们合到一个节点中,分别保存在节点的exact和inclusive下,这一步的目的实际是去重,为后面的建立排序树做准备 */
if (ngx_http_join_exact_locations(cf, locations) != ngx_ok) {
return ngx_error;
}
/* 递归每个location节点,得到当前节点的名字为其前缀的location的列表,保存在当前节点的list字段下 */
ngx_http_create_locations_list(locations, ngx_queue_head(locations));
/* 递归建立location三叉排序树 */
pclcf->static_locations = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, 0);
if (pclcf->static_locations == null) {
return ngx_error;
}
return ngx_ok;
} 经过ngx_http_init_location()函数处理之后,locations队列已经是排好序的了,建立三叉树的过程的主要工作都在ngx_http_create_locations_list()和ngx_http_create_locations_tree()中完成,这2个 函数都是递归函数,第1个函数递归locations队列中的每个节点,得到以当前节点的名字为前缀的location,并保存在当前节点的list字段 下,例如,对下列location:
location /xyz {
}
location = /xyz {
}
location /xyza {
}
location /xyzab {
}
location /xyzb {
}
location /abc {
}
location /efg {
}
location /efgaa {
} 排序的结果为/abc /efg /efgaa =/xyz /xyz /xyza /xyzab /xyzb,去重后结果为 /abc /efg /efgaa /xyz /xyza /xyzab/xyzb,ngx_http_create_locations_list()执行后的结果为:
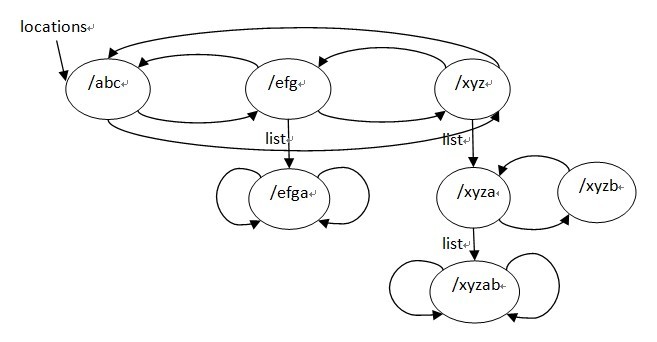
最后,来看下ngx_http_create_locations_tree函数:
static ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *
ngx_http_create_locations_tree(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_queue_t *locations,
size_t prefix)
{
...
/* 根节点为locations队列的中间节点 */
q = ngx_queue_middle(locations);
lq = (ngx_http_location_queue_t *) q;
len = lq->name->len - prefix;
node = ngx_palloc(cf->pool,
offsetof(ngx_http_location_tree_node_t, name) + len);
if (node == null) {
return null;
}
node->left = null;
node->right = null;
node->tree = null;
node->exact = lq->exact;
node->inclusive = lq->inclusive;
node->auto_redirect = (u_char) ((lq->exact && lq->exact->auto_redirect)
|| (lq->inclusive && lq->inclusive->auto_redirect));
node->len = (u_char) len;
ngx_memcpy(node->name, &lq->name->data[prefix], len);
/* 从中间节点开始断开 */
ngx_queue_split(locations, q, &tail);
if (ngx_queue_empty(locations)) {
/*
* ngx_queue_split() insures that if left part is empty,
* then right one is empty too
*/
goto inclusive;
}
/* 从locations左半部分得到左子树 */
node->left = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, locations, prefix);
if (node->left == null) {
return null;
}
ngx_queue_remove(q);
if (ngx_queue_empty(&tail)) {
goto inclusive;
}
/* 从locations右半部分得到右子树 */
node->right = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &tail, prefix);
if (node->right == null) {
return null;
}
inclusive:
if (ngx_queue_empty(&lq->list)) {
return node;
}
/* 从list队列得到tree子树 */
node->tree = ngx_http_create_locations_tree(cf, &lq->list, prefix + len);
if (node->tree == null) {
return null;
}
return node;
}
location tree节点的ngx_http_location_tree_node_s结构:
struct ngx_http_location_tree_node_s {
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *left;
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *right;
ngx_http_location_tree_node_t *tree;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *exact;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *inclusive;
u_char auto_redirect;
u_char len;
u_char name[1];
}; location tree结构用到的是left,right,tree 这3个字段, location tree实际上是一个三叉的字符串排序树,而且这里如果某个节点只考虑左,右子树,它是一颗平衡树,它的建立过程有点类似于一颗平衡排序二叉树的建立过程,先排序再用二分查找找到的节点顺序插入,ngx_http_location_tree_node_s的tree节点也是一颗平衡排序树,它是用该节点由ngx_http_create_locations_list()得到的list建立的,也就是该节点的名字是它的tree子树里面的所有节点名字的前缀,所以tree子树里面的所有节点的名字不用保存公共前缀,而且查找的时候,如果是转向tree节点的话,也是不需要再比较父节点的那段字符串了。
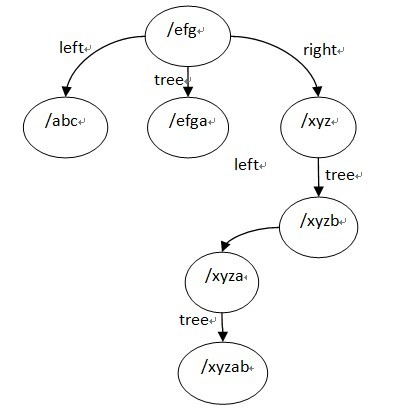
ngx_http_create_locations_tree()函数写的很清晰,它有一个参数是队列locations,它返回一颗三叉树,根节点为locations的中间节点,其左子树为locations队列的左半部分建立的location tree,右子树为location队列的右半部分建立的tree,tree节点为该根节点的list队列建立的tree。
最终建立的location tree如下(为了方便阅读,图中列出了tree节点的完整名字):
ps:关于 location modifier
1. =
这会完全匹配指定的 pattern ,且这里的 pattern 被限制成简单的字符串,也就是说这里不能使用正则表达式。
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location = /abcd {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 正好完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 如果运行 nginx server 的系统本身对大小写不敏感,比如 windows ,那么也匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),nginx 不认为这种情况是完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配,因为不是完全匹配
2. (none)
可以不写 location modifier ,nginx 仍然能去匹配 pattern 。这种情况下,匹配那些以指定的 patern 开头的 uri,注意这里的 uri 只能是普通字符串,不能使用正则表达式。
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location /abcd {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 正好完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 如果运行 nginx server 的系统本身对大小写不敏感,比如 windows ,那么也匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash)也属于匹配范围内 http://jb51.net/abcde # 仍然匹配,因为 uri 是以 pattern 开头的
3. ~
这个 location modifier 对大小写敏感,且 pattern 须是正则表达式
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location ~ ^/abcd$ {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 不匹配,~ 对大小写是敏感的 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),并不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$ http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$
注意:对于一些对大小写不敏感的系统,比如 windows ,~ 和 ~* 都是不起作用的,这主要是操作系统的原因。
4. ~*
与 ~ 类似,但这个 location modifier 不区分大小写,pattern 须是正则表达式
example:
server {
server_name jb51.net;
location ~* ^/abcd$ {
[…]
}
}匹配情况:
http://jb51.net/abcd # 完全匹配 http://jb51.net/abcd # 匹配,这就是它不区分大小写的特性 http://jb51.net/abcd?param1¶m2 # 忽略查询串参数(query string arguments),这里就是 /abcd 后面的 ?param1¶m2 http://jb51.net/abcd/ # 不匹配,因为末尾存在反斜杠(trailing slash),并不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$ http://jb51.net/abcde # 不匹配正则表达式 ^/abcd$
5. ^~
匹配情况类似 2. (none) 的情况,以指定匹配模式开头的 uri 被匹配,不同的是,一旦匹配成功,那么 nginx 就停止去寻找其他的 location 块进行匹配了(与 location 匹配顺序有关)
6. @
用于定义一个 location 块,且该块不能被外部 client 所访问,只能被 nginx 内部配置指令所访问,比如 try_files or error_page






























