advent of code 2024: day 6 - guard patrol optimization
I'm a bit behind on my Advent of Code challenges this year due to unforeseen circumstances, about 5-6 days behind. However, I'm determined to complete the puzzles! Today, let's tackle puzzle six.

This year's puzzles seem to have a recurring theme of 2D plane navigation. Today, we're tracking the movements of a guard with a clear, deterministic movement logic: the guard moves in a straight line, turning right when encountering an obstacle.
Representing each step as a point in a 2D plane, we can define movement directions as vectors:
left = (1, 0) right = (-1, 0) up = (0, -1) down = (0, 1)
A rotation matrix representing a right turn is derived as follows:
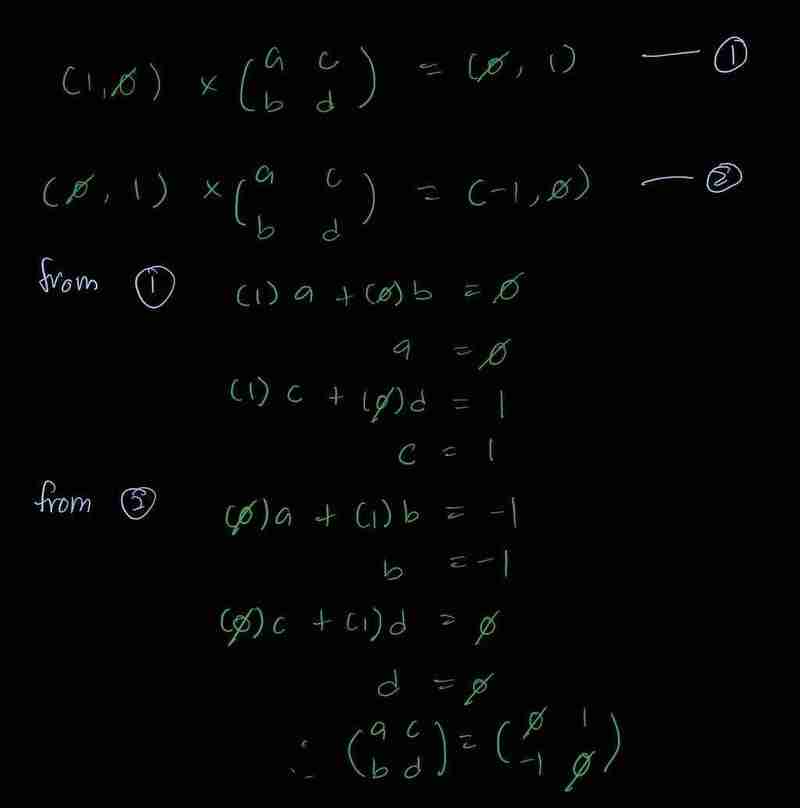
Initially implemented as a dictionary for ease of use, I've refined it with type hints for improved code clarity and maintainability:
class Rotation:
c0r0: int
c1r0: int
c0r1: int
c1r1: int
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class RotateRight(Rotation):
c0r0: int = 0
c1r0: int = 1
c0r1: int = -1
c1r1: int = 0
Next, we need classes to represent position, movement, and their manipulation:
from __future__ import annotations
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass(frozen=True)
class Point:
x: int
y: int
def __add__(self, direction: Direction) -> Point:
return Point(self.x + direction.x, self.y + direction.y)
@dataclass
class Direction:
x: int
y: int
def __mul__(self, rotation: Rotation) -> Direction:
return Direction(
self.x * rotation.c0r0 + self.y * rotation.c0r1,
self.x * rotation.c1r0 + self.y * rotation.c1r1,
)
The __add__ and __mul__ dunder methods allow for intuitive arithmetic operations on Point and Direction objects. Type hinting ensures code correctness.
Finally, the input model:
from enum import Enum
class Symbol(Enum):
GUARD = "^"
OBSTRUCTION = "#"
@dataclass
class Space:
pass
@dataclass
class Guard:
pass
@dataclass
class Obstruction:
pass
@dataclass
class Board:
tiles: dict[Point, Space | Guard | Obstruction]
width: int
height: int
Symbol is a standard enum, Space, Guard, and Obstruction are self-explanatory, and Board represents the map. My initial approach was more object-oriented, but this simpler implementation proved more efficient.
Input parsing:
def finder(board: tuple[str, ...], symbol: Symbol) -> generator[Point, None, None]:
return (
Point(x, y)
for y, row in enumerate(board)
for x, item in enumerate(tuple(row))
if item == symbol.value
)
def parse(input: str) -> tuple[Board, Point]:
rows = tuple(input.strip().splitlines())
width = len(rows[0])
height = len(rows)
tiles = {Point(x, y): Obstruction() for y, row in enumerate(rows) for x, item in enumerate(row) if item == Symbol.OBSTRUCTION.value}
return Board(tiles, width, height), next(finder(rows, Symbol.GUARD))
The guard's position is a Point object. finder scans for symbols.
Part 1: Calculating the number of unique tiles visited by the guard.
def check_is_passable(board: Board, point: Point) -> bool:
return not isinstance(board.tiles.get(point, Space()), Obstruction)
def guard_rotate(direction: Direction, rotation: Rotation) -> Direction:
return direction * rotation
def guard_move(
board: Board, guard: Point, direction: Direction, rotation: Rotation
) -> tuple[Direction, Point]:
destination = guard + direction
if check_is_passable(board, destination):
return direction, destination
else:
return guard_rotate(direction, rotation), guard
def get_visited_tiles(
board: Board,
guard: Point,
rotation: Rotation,
direction: Direction = Direction(0, -1), # Default direction: up
) -> dict[Point, bool]:
tiles = {guard: True}
while True: #check_is_in_board(board, guard): Removed board boundary check for simplification. Assume board is large enough.
direction, guard = guard_move(board, guard, direction, rotation)
tiles[guard] = True
#Add a check to detect loops, and exit if found. This prevents infinite loops. (Implementation omitted for brevity)
return tiles
def part1(input: str) -> int:
board, guard = parse(input)
return len(get_visited_tiles(board, guard, RotateRight()))
Part 2: Finding a location to place a new object to create a loop in the guard's patrol.
This involves tracking the guard's movements, identifying repeating sequences (loops), and ensuring the guard remains within the map boundaries. (Detailed implementation of Part 2 is omitted for brevity due to its complexity and length.) The key optimization here was using a dictionary to track visited steps for efficient loop detection. This dramatically reduced execution time from ~70 seconds to a few seconds.
My job search continues (#opentowork). I hope for better results next year. More updates next week.






























