本文介绍DDRNet语义分割模型,其属双路径结构,含高低分辨率两个分支,分别保存细节与提取上下文信息,通过Bilateral fusion模块融合特征,引入DAPPM模块和辅助损失。复现的DDRNet - 23在Cityscapes验证集mIoU达79.85%,优于目标值,已被paddleseg收录。
☞☞☞AI 智能聊天, 问答助手, AI 智能搜索, 免费无限量使用 DeepSeek R1 模型☜☜☜

paper:Deep Dual-resolution Networks for Real-time and Accurate Semantic Segmentation of Road Scenes
github:https://github.com/ydhongHIT/DDRNet
复现地址:https://github.com/justld/DDRNet_paddle
轻量级语义分割模型大致分为2类:Encoder-Decoder结构(如ESPNet)和two-pathway(如BiSeNet)。类似two-pathway结构,DDRNet使用Dual-resolution,并引入DAPPM( Deep Aggregation Pyramid Pooling Module)模块。在Cityscapes测试集、GPU 2080Ti,DDRNet-23-slim达到102FPS,miou77.4%。本项目复现了DDRNet_23,在cityscapes val miou 为79.85%,该算法已被paddleseg收录。
模型预测效果(来自cityscapes val):
下图为语义分割模型的几种结构:
(a)空洞卷积:通过空洞卷积增加模型的感受野,保留高分辨率的特征图降低信息损失;(Deeplab系列)
(b)Encoder-Decoder:通过Encoder(backbone)提取不同分辨率的特征图,然后将不同分辨率的特征图上采样融合,可以通过更换backbone来控制模型的大小;(UNet、ESPNet)
(c)Two-pathway:模型包含2个path,一个path负责提取上下文语义信息,一个path保留细节信息,然后将2个path输出融合。(BiSeNetV1、V2)
(d)DDRNet结构,具体见下文。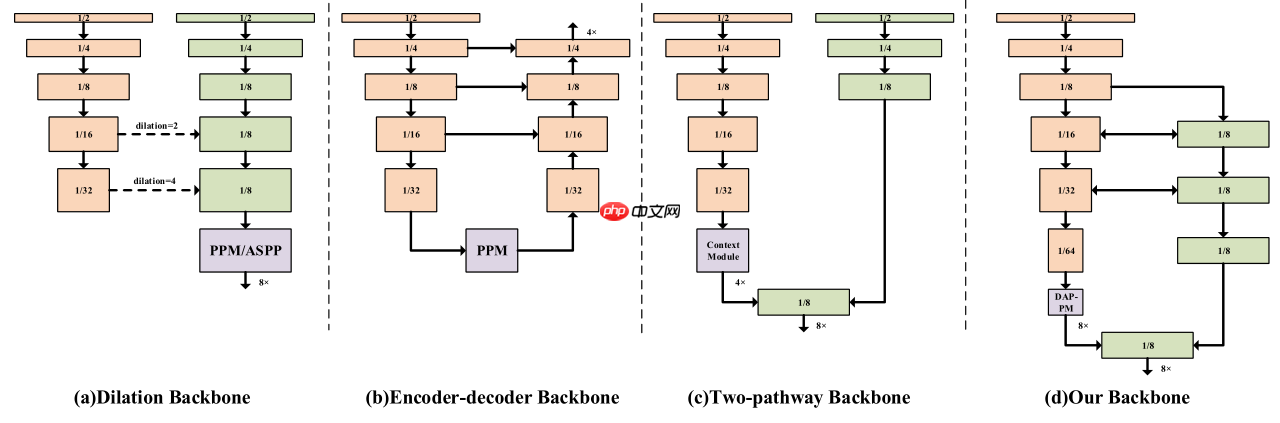
DDRNet网络结构如下图所示,模型包含2个分支,上面的分支分辨率较高,保存细节信息,下面的分支分辨率较低,用来提取上下文信息(使用了DAPPM模块增加其感受野),分支间特征融合使用Bilateral fusion模块,另外引入辅助损失函数。
DDRNet为了结合不同分辨率的特征图,使用了Bilateral fusion模块,不同分支不同分辨率的特征图分别通过上采样下采样后相加,保持自身分辨率不变的同时融合了另一分支的信息。
DAPPM为了获得多尺度信息,对输入特征图进行池化(核大小和步长不同),然后将不同大小的特征图上采样融合。
PS:池化部分类似PSPNet提出的Pyramid Pooling Module,整体结构类似ESPNetV2提出的EESP模块,具体可参考相关论文。 
pytorch源码:
class DAPPM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplanes, branch_planes, outplanes):
super(DAPPM, self).__init__()
self.scale1 = nn.Sequential(nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=5, stride=2, padding=2),
BatchNorm2d(inplanes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, branch_planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
)
self.scale2 = nn.Sequential(nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=9, stride=4, padding=4),
BatchNorm2d(inplanes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, branch_planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
)
self.scale3 = nn.Sequential(nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=17, stride=8, padding=8),
BatchNorm2d(inplanes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, branch_planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
)
self.scale4 = nn.Sequential(nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
BatchNorm2d(inplanes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, branch_planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
)
self.scale0 = nn.Sequential(
BatchNorm2d(inplanes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, branch_planes, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
)
self.process1 = nn.Sequential(
BatchNorm2d(branch_planes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(branch_planes, branch_planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
)
self.process2 = nn.Sequential(
BatchNorm2d(branch_planes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(branch_planes, branch_planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
)
self.process3 = nn.Sequential(
BatchNorm2d(branch_planes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(branch_planes, branch_planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
)
self.process4 = nn.Sequential(
BatchNorm2d(branch_planes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(branch_planes, branch_planes, kernel_size=3, padding=1, bias=False),
)
self.compression = nn.Sequential(
BatchNorm2d(branch_planes * 5, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(branch_planes * 5, outplanes, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
BatchNorm2d(inplanes, momentum=bn_mom),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, outplanes, kernel_size=1, bias=False),
) def forward(self, x):
#x = self.downsample(x)
width = x.shape[-1]
height = x.shape[-2]
x_list = []
x_list.append(self.scale0(x))
x_list.append(self.process1((F.interpolate(self.scale1(x),
size=[height, width],
mode='bilinear')+x_list[0])))
x_list.append((self.process2((F.interpolate(self.scale2(x),
size=[height, width],
mode='bilinear')+x_list[1]))))
x_list.append(self.process3((F.interpolate(self.scale3(x),
size=[height, width],
mode='bilinear')+x_list[2])))
x_list.append(self.process4((F.interpolate(self.scale4(x),
size=[height, width],
mode='bilinear')+x_list[3])))
out = self.compression(torch.cat(x_list, 1)) + self.shortcut(x) return out
cityscapes在cityscapes验证集和测试集上的表现如下: 
本次复现的目标是DDRNet-23 在cityscapes验证集 mIOU= 79.5%,复现的miou为79.85%。详情见下表:
| Model | Backbone | Resolution | Training Iters | mIoU | mIoU (flip) | mIoU (ms+flip) | Links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DDRNet_23 | - | 1024x1024 | 120000 | 79.85% | 80.11% | 80.44% | model|log|vdl |
运行以下cell,快速体验DDRNet-23。
# step 1: unzip data%cd ~/PaddleSeg/ !mkdir data !tar -xf ~/data/data64550/cityscapes.tar -C data/ %cd ~/
# step 2: 训练%cd ~/PaddleSeg
!python train.py --config configs/ddrnet/ddrnet23_cityscapes_1024x1024_120k.yml \
--do_eval --use_vdl --log_iter 100 --save_interval 4000 --save_dir output# step 3: val%cd ~/PaddleSeg/
!python val.py \
--config configs/ddrnet/ddrnet23_cityscapes_1024x1024_120k.yml \
--model_path output/best_model/model.pdparams# step 4: val flip%cd ~/PaddleSeg/
!python val.py \
--config configs/ddrnet/ddrnet23_cityscapes_1024x1024_120k.yml \
--model_path output/best_model/model.pdparams \
--aug_eval \
--flip_horizontal# step 5: val ms flip %cd ~/PaddleSeg/
!python val.py \
--config configs/ddrnet/ddrnet23_cityscapes_1024x1024_120k.yml \
--model_path output/best_model/model.pdparams \
--aug_eval \
--scales 0.75 1.0 1.25 \
--flip_horizontal# step 6: 预测, 预测结果在~/PaddleSeg/output/result文件夹内%cd ~/PaddleSeg/
!python predict.py \
--config configs/ddrnet/ddrnet23_cityscapes_1024x1024_120k.yml \
--model_path output/best_model/model.pdparams \
--image_path data/cityscapes/leftImg8bit/val/frankfurt/frankfurt_000000_000294_leftImg8bit.png \
--save_dir output/result# step 7: export%cd ~/PaddleSeg
!python export.py \
--config configs/ddrnet/ddrnet23_cityscapes_1024x1024_120k.yml \
--model_path output/best_model/model.pdparams \
--save_dir output# test tipc 1: prepare data%cd ~/PaddleSeg/ !bash test_tipc/prepare.sh ./test_tipc/configs/ddrnet/train_infer_python.txt 'lite_train_lite_infer'
# test tipc 2: pip install%cd ~/PaddleSeg/test_tipc/ !pip install -r requirements.txt
# test tipc 3: 安装auto_log%cd ~/ !git clone https://github.com/LDOUBLEV/AutoLog %cd AutoLog/ !pip3 install -r requirements.txt !python3 setup.py bdist_wheel !pip3 install ./dist/auto_log-1.2.0-py3-none-any.whl
# test tipc 4: test train inference%cd ~/PaddleSeg/ !bash test_tipc/test_train_inference_python.sh ./test_tipc/configs/ddrnet/train_infer_python.txt 'lite_train_lite_infer'
以上就是【第六期论文复现赛-语义分割】DDRNet的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号