本文介绍PointNet++在PaddlePaddle的复现项目。PointNet++通过分层结构提取点云局部特征,解决点集分布不均问题。复现基于ModelNet40数据集,top-1 Acc达92.0,超原论文。说明环境依赖、快速开始步骤,分析代码结构及复现中PaddlePaddle多维索引支持不足的问题与解决方法。
☞☞☞AI 智能聊天, 问答助手, AI 智能搜索, 免费无限量使用 DeepSeek R1 模型☜☜☜

Paper: PointNet++: Deep Hierarchical Feature Learning on Point Sets in a Metric Space
PointNet++与PointNet相比网络可以更好的提取局部特征。网络使用空间距离(metric space distances),使用PointNet对点集局部区域进行特征迭代提取,使其能够学到局部尺度越来越大的特征。基于自适应密度的特征提取方法,解决了点集分布不均匀的问题。
PointNet++
论文主要解决的是点云分割与点云分类的问题。该方法对PointNet进行了改进。针对PointNet存在的无法获得局部特征,难以对复杂场景进行分析的缺点。PointNet++,通过两个主要的方法进行了改进:
在PointNet++中,作者利用所在空间的距离度量将点集划分(partition)为有重叠的局部区域(可以理解为patch)。在此基础上,在小范围中从几何结构中提取局部特征(浅层特征),然后扩大范围,在这些局部特征的基础上提取更高层次的特征,从而提取到整个点集的全局特征。
PointNet++解决了两个关键的问题:第一,将点集划分为不同的区域;第二,利用特征提取器获取不同区域的局部特征。
在本文中,作者使用了PointNet作为特征提取器,使用邻域球来定义分区,每个区域可以通过中心坐标和半径来确定。中心坐标的选取,作者使用了快速采样算法来完成(farthest point sampling (FPS) algorithm)。区域半径的选择使用了Multi-scale grouping (MSG) and Multi-resolution grouping (MRG)来实现。
PointNet++是PointNet的延伸,在PointNet的基础上加入了多层次结构(hierarchical structure),使得网络能够在越来越大的区域上提供更高级别的特征。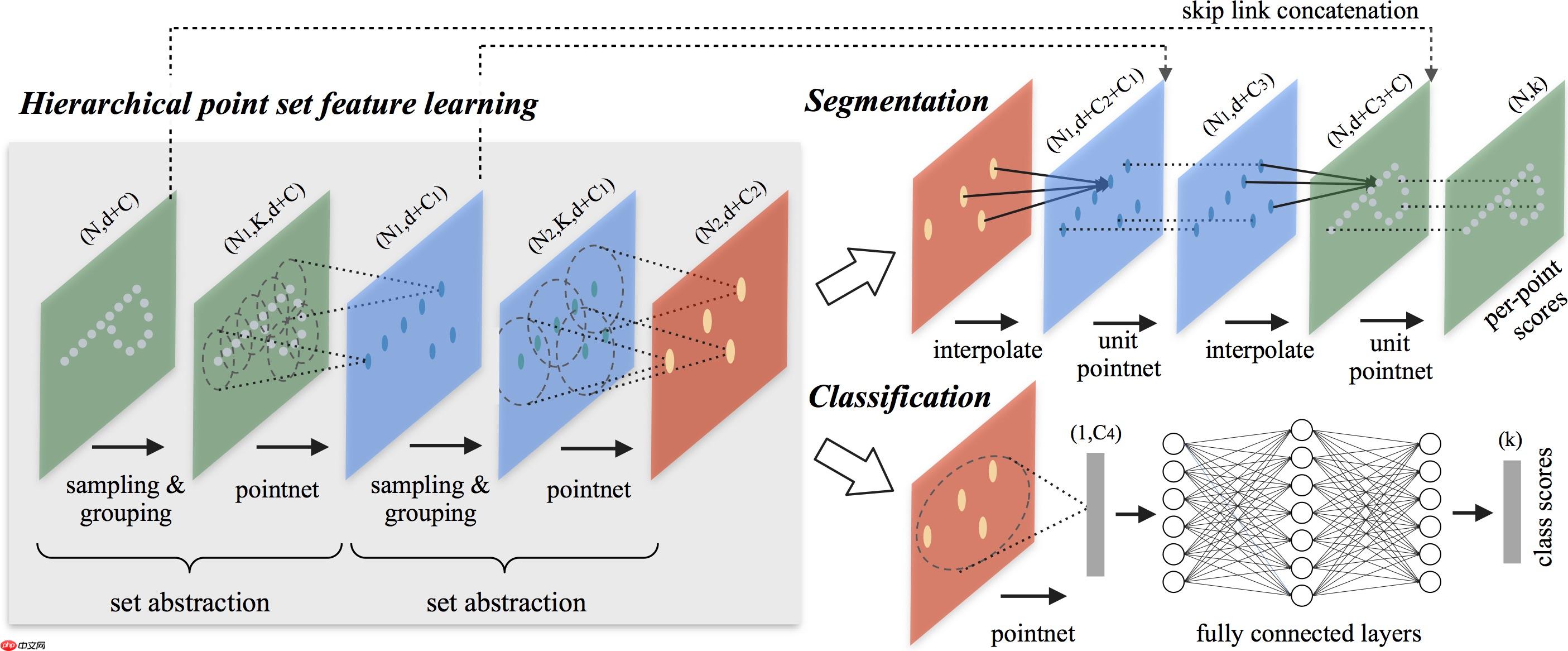
网络的每一组set abstraction layers主要包括3个部分:Sampling layer, Grouping layer and PointNet layer。
· Sample layer:主要是对输入点进行采样,在这些点中选出若干个中心点; · Grouping layer:是利用上一步得到的中心点将点集划分成若干个区域; · PointNet layer:是对上述得到的每个区域进行编码,变成特征向量。 每一组提取层的输入是N * (d + C),其中N是输入点的数量,d是坐标维度,C是特征维度。输出是N'* (d + C'),其中N'是输出点的数量,d是坐标维度不变,C'是新的特征维度。
| 指标 | 原论文 | 复现精度 |
|---|---|---|
| top-1 Acc | 90.7 | 92.0 |
使用的数据集为:ModelNet40。
ModelNet包含了来自662类的127915个三维形状,其子集Model10包含了来自10类的4899个三维形状,ModelNet40包含了来自40类的12311个三维形状。ModelNet40是常用的三维点云分割数据集,现在是一个用来评判三维点云分割性能的常规benchmark。
硬件:GPU、CPU
框架:
Download alignment ModelNet and put it in ./dataset/modelnet40_normal_resampled/
python train_modelnet.py --process_data
python test_modelnet.py --log_dir path_to_model
|—— README.md|—— provider.py # 点云数据增强|—— ModelNetDataset.py # 数据集定义及加载|── train_modelnet.py # 训练网络|── test_modelnet.py # 测试网络|—— models # 模型文件定义
可以在 train_modelnet.py 中设置训练与评估相关参数,具体如下:
| 参数 | 默认值 | 说明 | 其他 |
|---|---|---|---|
| batch_size | 24 | batch_size 大小 | |
| epoch | 200, 可选 | epoch次数 | |
| batch_size | 32, 可选 | batch_size 大小 | |
| learning_rate | 0.001, 可选 | 初始学习率 | |
| num_point | 1024, 可选 | 采样的点的个数 | |
| decay_rate | 1e-4, 可选 | weight decay | |
| use_normals | False, 可选 | normalize 点 | |
| use_uniform_sample | False, 可选 | 均匀采样 | |
| process_data | False, 可选 | 是否预处理数据,如果没有下载预处理的数据需要为true |
Reference Implementation:
复现主要参考的是PyTorch的pytorch实现,pytorch的大部分api可以在paddlepaddle中找到对应,最困难的地方在于,paddlepaddle没法办法进行二维的索引,对应原实现中的多个部分
def index_points(points, idx):
"""
Input:
points: input points data, [B, N, C]
idx: sample index data, [B, S]
Return:
new_points:, indexed points data, [B, S, C]
"""
device = points.device
B = points.shape[0]
view_shape = list(idx.shape)
view_shape[1:] = [1] * (len(view_shape) - 1)
repeat_shape = list(idx.shape)
repeat_shape[0] = 1
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(view_shape).repeat(repeat_shape)
new_points = points[batch_indices, idx, :] return new_points
def farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint):
"""
Input:
xyz: pointcloud data, [B, N, 3]
npoint: number of samples
Return:
centroids: sampled pointcloud index, [B, npoint]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
centroids = torch.zeros(B, npoint, dtype=torch.long).to(device)
distance = torch.ones(B, N).to(device) * 1e10
farthest = torch.randint(0, N, (B,), dtype=torch.long).to(device)
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device) for i in range(npoint):
centroids[:, i] = farthest
centroid = xyz[batch_indices, farthest, :].view(B, 1, 3)
dist = torch.sum((xyz - centroid) ** 2, -1)
mask = dist < distance
distance[mask] = dist[mask]
farthest = torch.max(distance, -1)[1] return centroids
def query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz):
"""
Input:
radius: local region radius
nsample: max sample number in local region
xyz: all points, [B, N, 3]
new_xyz: query points, [B, S, 3]
Return:
group_idx: grouped points index, [B, S, nsample]
"""
device = xyz.device
B, N, C = xyz.shape
_, S, _ = new_xyz.shape
group_idx = torch.arange(N, dtype=torch.long).to(device).view(1, 1, N).repeat([B, S, 1])
sqrdists = square_distance(new_xyz, xyz)
group_idx[sqrdists > radius ** 2] = N
group_idx = group_idx.sort(dim=-1)[0][:, :, :nsample]
group_first = group_idx[:, :, 0].view(B, S, 1).repeat([1, 1, nsample])
mask = group_idx == N
group_idx[mask] = group_first[mask] return group_idx
def sample_and_group(npoint, radius, nsample, xyz, points, returnfps=False):
"""
Input:
npoint:
radius:
nsample:
xyz: input points position data, [B, N, 3]
points: input points data, [B, N, D]
Return:
new_xyz: sampled points position data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3]
new_points: sampled points data, [B, npoint, nsample, 3+D]
"""
B, N, C = xyz.shape
S = npoint
fps_idx = farthest_point_sample(xyz, npoint) # [B, npoint, C]
new_xyz = index_points(xyz, fps_idx)
idx = query_ball_point(radius, nsample, xyz, new_xyz)
grouped_xyz = index_points(xyz, idx) # [B, npoint, nsample, C]
grouped_xyz_norm = grouped_xyz - new_xyz.view(B, S, 1, C) if points is not None:
grouped_points = index_points(points, idx)
new_points = torch.cat([grouped_xyz_norm, grouped_points], dim=-1) # [B, npoint, nsample, C+D]
else:
new_points = grouped_xyz_norm if returnfps: return new_xyz, new_points, grouped_xyz, fps_idx else: return new_xyz, new_points
这里所有的二维索引都没有办法使用,包括经常使用的mask方法
这里进行了一些妥协,将需要二维索引的地方进行拉直,从而可以将二维索引变为n个一维索引,但是这里肯定对速度有所损失,暂时没有想到好的办法
farthest = torch.randint(0, N, (B,), dtype=torch.long).to(device)
batch_indices = torch.arange(B, dtype=torch.long).to(device)for i in range(npoint):
centroids[:, i] = farthest
centroid = xyz[batch_indices, farthest, :].view(B, 1, 3)
farthest = paddle.randint(0, N, (B, ), dtype="int64")for i in range(npoint):
centroids[:, i] = farthest # centroid = xyz[batch_indices, farthest, :].reshape((B, 1, 3))
centroid = paddle.zeros((B, 1, 3), dtype="float32") for j in range(3):
centroid[:,:,j] = xyz[:,:,j].index_sample(farthest.reshape((-1, 1))).reshape((B, 1))
对于mask的地方,可以直接使用数值运算的方法达到mask的目的
mask = dist < distance distance[mask] = dist[mask] farthest = torch.max(distance, -1)[1]
mask = dist < distance
mask = mask.astype("int64")
mask_index = paddle.nonzero(mask)if mask_index.size > 0:
distance = distance * (1 - mask.astype("float32")) + dist * mask.astype("float32")
目前的paddlepaddle可以支持大多数pytorch的API,但是其对于多维索引的支持不足,非常影响使用体验,而多维索引又是一个在日常的研究以及工程中,非常常规的功能,这里需要改进。
!python3 -m pip install tqdm
%cd /home/aistudio/data/data50045/ !unzip modelnet40_normal_resampled.zip
%cd /home/aistudio/ !unzip pointnet_plus_plus_paddlepaddle-main.zip%cd pointnet_plus_plus_paddlepaddle-main/
%mkdir /home/aistudio/pointnet_plus_plus_paddlepaddle-main/dataset %cp -r /home/aistudio/data/data50045/modelnet40_normal_resampled /home/aistudio/pointnet_plus_plus_paddlepaddle-main/dataset
%cd /home/aistudio/pointnet_plus_plus_paddlepaddle-main/ !python3 train_modelnet.py --process_data
%cd /home/aistudio/pointnet_plus_plus_paddlepaddle-main/ !python3 test_modelnet.py --log_dir path_to_log
以上就是点云处理: 基于飞桨复现PointNet++的详细内容,更多请关注php中文网其它相关文章!

每个人都需要一台速度更快、更稳定的 PC。随着时间的推移,垃圾文件、旧注册表数据和不必要的后台进程会占用资源并降低性能。幸运的是,许多工具可以让 Windows 保持平稳运行。

Copyright 2014-2025 https://www.php.cn/ All Rights Reserved | php.cn | 湘ICP备2023035733号